The expression of YAP1 and other transcription factors contributes to lineage plasticity in combined small cell lung carcinoma
- PMID: 39283755
- PMCID: PMC11404481
- DOI: 10.1002/2056-4538.70001
The expression of YAP1 and other transcription factors contributes to lineage plasticity in combined small cell lung carcinoma
Abstract
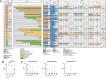
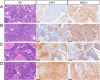
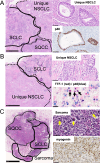
Lineage plasticity in small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) causes therapeutic difficulties. This study aimed to investigate the pathological findings of plasticity in SCLC, focusing on combined SCLC, and elucidate the involvement of YAP1 and other transcription factors. We analysed 100 surgically resected SCLCs through detailed morphological observations and immunohistochemistry for YAP1 and other transcription factors. Component-by-component next-generation sequencing (n = 15 pairs) and immunohistochemistry (n = 35 pairs) were performed on the combined SCLCs. Compared with pure SCLCs (n = 65), combined SCLCs (n = 35) showed a significantly larger size, higher expression of NEUROD1, and higher frequency of double-positive transcription factors (p = 0.0009, 0.04, and 0.019, respectively). Notably, 34% of the combined SCLCs showed morphological mosaic patterns with unclear boundaries between the SCLC and its partner. Combined SCLCs not only had unique histotypes as partners but also represented different lineage plasticity within the partner. NEUROD1-dominant combined SCLCs had a significantly higher proportion of adenocarcinomas as partners, whereas POU2F3-dominant combined SCLCs had a significantly higher proportion of squamous cell carcinomas as partners (p = 0.006 and p = 0.0006, respectively). YAP1 expression in SCLC components was found in 80% of combined SCLCs and 62% of pure SCLCs, often showing mosaic-like expression. Among the combined SCLCs with component-specific analysis, the identical TP53 mutation was found in 10 pairs, and the identical Rb1 abnormality was found in 2 pairs. On immunohistochemistry, the same abnormal p53 pattern was found in 34 pairs, and Rb1 loss was found in 24 pairs. In conclusion, combined SCLC shows a variety of pathological plasticity. Although combined SCLC is more plastic than pure SCLC, pure SCLC is also a phenotypically plastic tumour. The morphological mosaic pattern and YAP1 mosaic-like expression may represent ongoing lineage plasticity. This study also identified the relationship between transcription factors and partners in combined SCLC. Transcription factors may be involved in differentiating specific cell lineages beyond just 'neuroendocrine'.
Keywords: YAP1; combined small cell lung carcinoma; molecular marker; mosaic; plasticity; small cell carcinoma; small cell lung carcinoma; transcription factors.
© 2024 The Author(s). The Journal of Pathology: Clinical Research published by The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Watanabe K, Kage H, Shinozaki‐Ushiku A, et al. Spontaneous transdifferentiation from small cell lung carcinoma to squamous cell carcinoma. J Thorac Oncol 2019; 14: e31–e34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

