Multifaceted activation of STING axis upon Nipah and measles virus-induced syncytia formation
- PMID: 39283943
- PMCID: PMC11426520
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012569
Multifaceted activation of STING axis upon Nipah and measles virus-induced syncytia formation
Abstract
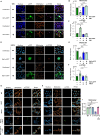
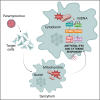
Activation of the DNA-sensing STING axis by RNA viruses plays a role in antiviral response through mechanisms that remain poorly understood. Here, we show that the STING pathway regulates Nipah virus (NiV) replication in vivo in mice. Moreover, we demonstrate that following both NiV and measles virus (MeV) infection, IFNγ-inducible protein 16 (IFI16), an alternative DNA sensor in addition to cGAS, induces the activation of STING, leading to the phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 and the production of IFNβ and interleukin 6. Finally, we found that paramyxovirus-induced syncytia formation is responsible for loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and leakage of mitochondrial DNA in the cytoplasm, the latter of which is further detected by both cGAS and IFI16. These results contribute to improve our understanding about NiV and MeV immunopathogenesis and provide potential paths for alternative therapeutic strategies.
Copyright: © 2024 Amurri et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

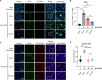
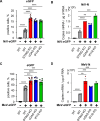
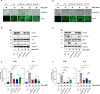
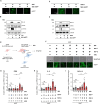

References
-
- Chen C, Xu P. Cellular functions of cGAS-STING signaling. Trends Cell Biol. 2022. Nov 24;S0962–8924(22)00252–5. - PubMed
-
- Gentili M, Lahaye X, Nadalin F, Nader GPF, Puig Lombardi E, Herve S, et al. The N-Terminal Domain of cGAS Determines Preferential Association with Centromeric DNA and Innate Immune Activation in the Nucleus. Cell Rep. 2019. Feb 26;26(9):2377–2393.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.105 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

