Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin affects neutrophil effector functions via cAMP/PKA/ERK signaling
- PMID: 39284098
- PMCID: PMC11407407
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2399215
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli heat labile enterotoxin affects neutrophil effector functions via cAMP/PKA/ERK signaling
Abstract
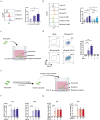
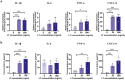
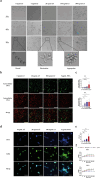
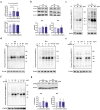
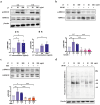
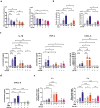
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) are a major cause of diarrheal illness in humans and animals, induced by enterotoxins produced by these pathogens. Despite the crucial role of neutrophils in combatting bacterial infections, our understanding of how enterotoxins impact neutrophil function is limited. To address this knowledge gap, we used heat-labile enterotoxin (LT) and heat-stable enterotoxin a (STa) to investigate their impact on the effector functions of neutrophils. Our study reveals that pSTa does not exert any discernible effect on the function of neutrophils. In contrast, LT altered the migration and phagocytosis of neutrophils and induced the production of inflammatory factors via activation of cAMP/PKA and ERK1/2 signaling. LT also attenuated the release of neutrophil extracellular traps by neutrophils via the PKA signaling pathway. Our findings provide novel insights into the impact of LT on neutrophil function, shedding light on the underlying mechanisms that govern its immunoregulatory effects. This might help ETEC in subverting the immune system and establishing infection.
Keywords: ETEC; Heat labile enterotoxin; cAMP/PKA/ERK signaling; neutrophils; pig.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures



References
-
- Anderson JD, Bagamian KH, Muhib F, Amaya MP, Laytner LA, Wierzba T, Rheingans R.. Burden of enterotoxigenic and shigella non-fatal diarrhoeal infections in 79 low-income and lower middle-income countries: a modelling analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(3):E321–23. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109x(18)30483-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Luppi A, Gibellini M, Gin T, Vangroenweghe F, Vandenbroucke V, Bauerfeind R, Bonilauri P, Labarque G, Hidalgo Á. Prevalence of virulence factors in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from pigs with post-weaning diarrhoea in Europe. Porcine Health Manag. 2016;2(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s40813-016-0039-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
