An intranasal cationic liposomal polysaccharide vaccine elicits humoral immune responses against Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 39284859
- PMCID: PMC11405767
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-06806-1
An intranasal cationic liposomal polysaccharide vaccine elicits humoral immune responses against Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
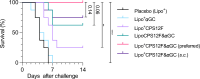
Diseases caused by S. pneumoniae are the leading cause of child mortality. As antibiotic resistance of S. pneumoniae is rising, vaccination remains the most recommended solution. However, the existing pneumococcal polysaccharides vaccine (Pneumovax® 23) proved only to induce T-independent immunity, and strict cold chain dependence of the protein conjugate vaccine impedes its promotion in developing countries, where infections are most problematic. Affordable and efficient vaccines against pneumococcus are therefore in high demand. Here, we present an intranasal vaccine Lipo+CPS12F&αGC, containing the capsular polysaccharides of S. pneumoniae 12F and the iNKT agonist α-galactosylceramide in cationic liposomes. In BALB/cJRj mice, the vaccine effectively activates iNKT cells and promotes B cells maturation, stimulates affinity-matured IgA and IgG production in both the respiratory tract and systemic blood, and displays sufficient protection both in vivo and in vitro. The designed vaccine is a promising, cost-effective solution against pneumococcus, which can be expanded to cover more serotypes and pathogens.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Technical University of Denmark has filed a patent covering this technology, and the inventors are M.H.C., P.W., C.R., J.R.H., and A.E.H. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- World Health Organization. Pneumococcal disease. https://www.who.int/teams/health-product-policy-and-standards/standards-... (2024).
-
- Global Pneumococcal Sequencing Project. Serotype. https://www.pneumogen.net/gps/#/resources#serotypes (2024).
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Factsheet about pneumococcal disease. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/pneumococcal-disease/facts (2024).
-
- Merck. Effectiveness data for Pneumovax®23 (pneumococcal vaccine polyvalent). https://www.merckvaccines.com/pneumovax23/pneumococcal-vaccine-efficacy (2024).
-
- Emmadi, M. et al. A streptococcus pneumoniae type 2 oligosaccharide glycoconjugate elicits opsonic antibodies and is protective in an animal model of invasive pneumococcal disease. J. Am. Chem. Soc.139, 14783–14791 (2017). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R347-2020-2307/Lundbeckfonden (Lundbeck Foundation)
- NNF18OC0053048/Novo Nordisk Fonden (Novo Nordisk Foundation)
- NNF20OC0065094),/Novo Nordisk Fonden (Novo Nordisk Foundation)
- 9041-00080B/Teknologi og Produktion, Det Frie Forskningsråd (Technology and Production, Danish Council for Independent Research)
- CF22-1105/Carlsbergfondet (Carlsberg Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

