Antagonism between H3K27me3 and genome-lamina association drives atypical spatial genome organization in the totipotent embryo
- PMID: 39284976
- PMCID: PMC11525175
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01902-8
Antagonism between H3K27me3 and genome-lamina association drives atypical spatial genome organization in the totipotent embryo
Abstract
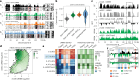
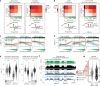
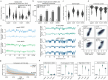
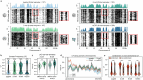
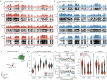
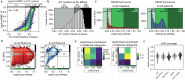
In mammals, early embryonic development exhibits highly unusual spatial positioning of genomic regions at the nuclear lamina, but the mechanisms underpinning this atypical genome organization remain elusive. Here, we generated single-cell profiles of lamina-associated domains (LADs) coupled with transcriptomics, which revealed a striking overlap between preimplantation-specific LAD dissociation and noncanonical broad domains of H3K27me3. Loss of H3K27me3 resulted in a restoration of canonical LAD profiles, suggesting an antagonistic relationship between lamina association and H3K27me3. Tethering of H3K27me3 to the nuclear periphery showed that the resultant relocalization is partially dependent on the underlying DNA sequence. Collectively, our results suggest that the atypical organization of LADs in early developmental stages is the result of a tug-of-war between intrinsic affinity for the nuclear lamina and H3K27me3, constrained by the available space at the nuclear periphery. This study provides detailed insight into the molecular mechanisms regulating nuclear organization during early mammalian development.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

