Cardiometabolic benefits of fenofibrate in heart failure related to obesity and diabetes
- PMID: 39285303
- PMCID: PMC11406805
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-024-02417-6
Cardiometabolic benefits of fenofibrate in heart failure related to obesity and diabetes
Abstract
Background: Heart failure (HF) is a serious and common condition affecting millions of people worldwide, with obesity being a major cause of metabolic disorders such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. This study aimed to investigate the effects of fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) agonist, on the obese- and diabetes-related cardiomyopathy.
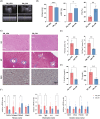
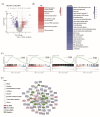
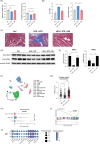
Methods and results: We used db/db mice and high fat diet-streptozotocin induced diabetic mice to investigate the underlying mechanisms of fenofibrate's beneficial effects on heart function. Fenofibrate reduced fibrosis, and lipid accumulation, and suppressed inflammatory and immunological responses in the heart via TNF signaling. In addition, we investigated the beneficial effects of fenofibrate on HF hospitalization. The Korean National Health Insurance database was used to identify 427,154 fenofibrate users and 427,154 non-users for comparison. During the 4.22-year follow-up, fenofibrate use significantly reduced the risk of HF hospitalization (hazard ratio, 0.907; 95% CI 0.824-0.998).
Conclusions: The findings suggest that fenofibrate may be a useful therapeutic agent for obesity- and diabetes-related cardiomyopathy.
Keywords: Diabetic cardiomyopathy; Fenofibrate; Heart failure.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Malik A, Brito D, Vaqar S, Chhabra L. Congestive heart failure. 2017. - PubMed
-
- Taylor CJ, Roalfe AK, Iles R, Hobbs FR. Ten-year prognosis of heart failure in the community: follow-up data from the Echocardiographic Heart of England Screening (ECHOES) study. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14(2):176–84. - PubMed
-
- Shah KS, Xu H, Matsouaka RA, Bhatt DL, Heidenreich PA, Hernandez AF, Devore AD, Yancy CW, Fonarow GC. Heart failure with preserved, borderline, and reduced ejection fraction: 5-year outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(20):2476–86. - PubMed
-
- Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Ventura HO. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;53(21):1925–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

