A cross domain access control model for medical consortium based on DBSCAN and penalty function
- PMID: 39285411
- PMCID: PMC11403857
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-024-02638-5
A cross domain access control model for medical consortium based on DBSCAN and penalty function
Abstract
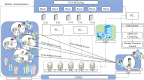
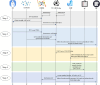
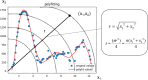
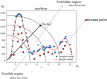
Graded diagnosis and treatment, referral, and expert consultations between medical institutions all require cross domain access to patient medical information to support doctors' treatment decisions, leading to an increase in cross domain access among various medical institutions within the medical consortium. However, patient medical information is sensitive and private, and it is essential to control doctors' cross domain access to reduce the risk of leakage. Access control is a continuous and long-term process, and it first requires verification of the legitimacy of user identities, while utilizing control policies for selection and management. After verifying user identity and access permissions, it is also necessary to monitor unauthorized operations. Therefore, the content of access control includes authentication, implementation of control policies, and security auditing. Unlike the existing focus on authentication and control strategy implementation in access control, this article focuses on the control based on access log security auditing for doctors who have obtained authorization to access medical resources. This paper designs a blockchain based doctor intelligent cross domain access log recording system, which is used to record, query and analyze the cross domain access behavior of doctors after authorization. Through DBSCAN clustering analysis of doctors' cross domain access logs, we find the abnormal phenomenon of cross domain access, and build a penalty function to dynamically control doctors' cross domain access process, so as to reduce the risk of Data breach. Finally, through comparative analysis and experiments, it is shown that the proposed cross domain access control model for medical consortia based on DBSCAN and penalty function has good control effect on the cross domain access behavior of doctors in various medical institutions of the medical consortia, and has certain feasibility for the cross domain access control of doctors.
Keywords: Access control; Blockchain technology; Medical consortium; Medical informatization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Novel model to authenticate role-based medical users for blockchain-based IoMT devices.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 10;19(7):e0304774. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304774. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38985779 Free PMC article.
-
A Blockchain-Based Authentication and Authorization Scheme for Distributed Mobile Cloud Computing Services.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 22;23(3):1264. doi: 10.3390/s23031264. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36772304 Free PMC article.
-
Blockchain-Enabled iWellChain Framework Integration With the National Medical Referral System: Development and Usability Study.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Dec 4;21(12):e13563. doi: 10.2196/13563. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31799935 Free PMC article.
-
Design of a Secure Medical Data Sharing Scheme Based on Blockchain.J Med Syst. 2020 Jan 8;44(2):52. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1468-1. J Med Syst. 2020. PMID: 31915982 Review.
-
A Blockchain Framework for Patient-Centered Health Records and Exchange (HealthChain): Evaluation and Proof-of-Concept Study.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Aug 31;21(8):e13592. doi: 10.2196/13592. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31471959 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-camera spatiotemporal deep learning framework for real-time abnormal behavior detection in dense urban environments.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 23;15(1):26813. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12388-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40702170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haowen Y, Li Y. Integrated medical theory, practice, and effectiveness evaluation at home and abroad. Chin J Evid Based Med. 2020;20(05):585–92.
-
- Lei Y, et al. Exploring strategies for responding to sudden public health incidents under the mode of group medical Alliance China. Hosp Manage. 2020;40(04):33–4.
-
- Yinying Y, et al. SWOT analysis and strategies for the development of traditional Chinese medicine consortia in China. Med Content. 2019;10(05):70–3.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

