LINC01133 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by upregulating CTNNB1 by acting as a sponge for miR-214-3p
- PMID: 39285416
- PMCID: PMC11406849
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-024-05053-8
LINC01133 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by upregulating CTNNB1 by acting as a sponge for miR-214-3p
Abstract
Background: Osteoporosis results from decreased bone mass and disturbed bone structure. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs) demonstrate robust osteogenic differentiation, a critical process for bone formation. This research was designed to examine the functions of LINC01133 in osteogenic differentiation.
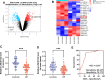
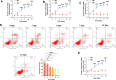
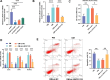
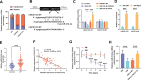
Methods: Differentially expressed lncRNAs affecting osteogenic differentiation in hBMSCs were identified from the GEO database. A total of 74 osteoporosis patients and 70 controls were enrolled. hBMSCs were stimulated to undergo osteogenic differentiation using an osteogenic differentiation medium (OM). RT-qPCR was performed to evaluate LINC01133 levels and osteogenesis-related genes such as osteocalcin, osteopontin, and RUNX2. An alkaline phosphates (ALP) activity assay was conducted to assess osteogenic differentiation. Cell apoptosis was detected using flow cytometry. Dual luciferase reporter assay and RIP assay were employed to investigate the association between miR-214-3p and LINC01133 or CTNNB1. Loss or gain of function assays were conducted to elucidate the impact of LINC01133 and miR-214-3p on osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs.
Results: LINC01133 and CTNNB1 expression decreased in osteoporotic patients but increased in OM-cultured hBMSCs, whereas miR-214-3p showed an opposite trend. Depletion of LINC01133 suppressed the expression of genes associated with bone formation and ALP activity triggered by OM in hBMSCs, leading to increased cell apoptosis. Nevertheless, this suppression was partially counteracted by the reduced miR-214-3p levels. Mechanistically, LINC01133 and CTNNB1 were identified as direct targets of miR-214-3p.
Conclusions: Our study highlights the role of LINC01133 in positively regulating CTNNB1 expression by inhibiting miR-214-3p, thereby promoting osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. These findings may provide valuable insights into bone regeneration in osteoporosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells; LINC01133; Osteogenic differentiation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel miR-466l-3p/FGF23 axis promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Bone. 2024 Aug;185:117123. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2024.117123. Epub 2024 May 11. Bone. 2024. PMID: 38735373
-
LINC00968 accelerates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the miR-17-5p/STAT3 axis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Mar 6;20(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-05627-0. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40050898 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HOTAIRM1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by targeting miR-152-3p/ETS1 axis.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):5597-5608. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08466-6. Epub 2023 May 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37171551
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived from Dental Tissues-Related lncRNAs: A New Regulator in Osteogenic Differentiation.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023 Jul 4;2023:4622584. doi: 10.1155/2023/4622584. eCollection 2023. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2023. PMID: 40226409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPK, a hub for the microenvironmental regulation of bone homeostasis and diseases.J Cell Physiol. 2024 Nov;239(11):e31393. doi: 10.1002/jcp.31393. Epub 2024 Aug 30. J Cell Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39210747 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

