Simultaneous removal and separate recovery of radioactive Cs+ and I- ions from wastewater using a reusable bifunctional composite, Ni@Pt/K2NiFe(CN)6
- PMID: 39286105
- PMCID: PMC11403085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37134
Simultaneous removal and separate recovery of radioactive Cs+ and I- ions from wastewater using a reusable bifunctional composite, Ni@Pt/K2NiFe(CN)6
Abstract
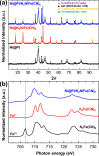
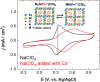
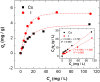
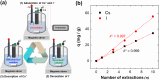
Radioactive Cs+ and I- ions are major components of nuclear wastewater, typically existing as counter ions. Due to their high water solubility and mobility, these ions can spread through contaminated water and soil into ecosystems, necessitating continuous removal and management. In this study, we synthesized a reusable bifunctional Ni@Pt/K2NiFe(CN)6 composite that can simultaneously remove radioactive Cs+ and I- ions and, for the first time, enable their separate recovery in aqueous solutions. In this material, K2NiFe(CN)6 acted as an electrochemically switched ion exchanger, controlling the adsorption/desorption of Cs+, while Pt enabled the spontaneous adsorption and electrochemical desorption of I-, and the magnetic Ni core allowed for efficient adsorbent recovery. The adsorption isotherms of both Cs+ and I- were best fitted using the Langmuir model, and the corresponding adsorption capacities were comparable to those of conventional adsorbents used for the separate removal of Cs+ and I-. Furthermore, the composite demonstrated stability over 100 sorption cycles, maintaining high recovery efficiencies of 97.9 % for Cs+ and 99.7 % for I-, thereby proving its reusability. Thus, the developed composite holds great promise for radioactive wastewater treatment and environmental restoration.
Keywords: Bifunctional composite; Cesium and iodine removal; Electrochemical control; Reusable; Separate recovery.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Sang-Eun Bae reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100003725National Research Foundation of Korea. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cesium removal from wastewater: High-efficient and reusable adsorbent K1.93Ti0.22Sn3S6.43.Chemosphere. 2022 Oct;305:135406. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135406. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 35728662
-
MXene/AgNW composite material for selective and efficient removal of radioactive cesium and iodine from water.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 11;13(1):19696. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-47075-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37952015 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ternary polymer composites of macroporous adsorbents on adsorption properties for heavy metal removal from aqueous solution.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Nov;29(55):84006-84018. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-21701-0. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35776300
-
A remotely steerable Janus micromotor adsorbent for the active remediation of Cs-contaminated water.J Hazard Mater. 2019 May 5;369:416-422. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.054. Epub 2019 Feb 14. J Hazard Mater. 2019. PMID: 30784971
-
Cesium adsorption from an aqueous medium for environmental remediation: A comprehensive analysis of adsorbents, sources, factors, models, challenges, and opportunities.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Nov 10;950:175368. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.175368. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 39122022 Review.
References
-
- Hong S., Bradshaw C.J.A., Brook B.W. Global zero-carbon energy pathways using viable mixes of nuclear and renewables. Appl. Energy. 2015;143:451–459.
-
- Mekonnen M.M., Gerbens-Leenes P.W., Hoekstra A.Y. The consumptive water footprint of electricity and heat: a global assessment. Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. 2015;1:285–297.
-
- Ten Hoeve J.E., Jacobson M.Z. Worldwide health effects of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012;5:8743–8757.
-
- Liu X., Wu J., Hou L.-a., Wang J. Fouling and cleaning protocols for forward osmosis membrane used for radioactive wastewater treatment. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2020;52:581–588.
-
- Deng D., Zhang L., Dong M., Samuel R.E., Ofori-Boadu A., Lamssali M. Radioactive waste: a review. Water Environ. Res. 2020;92:1818–1825. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

