Effect of different blanching methods on kinetics of physico-chemical, functional properties, and enzyme inactivation in baby corn
- PMID: 39286177
- PMCID: PMC11402913
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36964
Effect of different blanching methods on kinetics of physico-chemical, functional properties, and enzyme inactivation in baby corn
Abstract
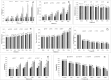
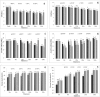
Baby corn, characterized by its high water activity and elevated respiration rate, poses a formidable obstacle to prolonged storage under standard ambient conditions and necessitates specialized treatments for transportation to distant locations. One of the primary postharvest challenges associated with baby corn is the occurrence of brown pigment formation because of enzymatic browning at the apex of its immature ovules, cut surfaces, and silk attached to the young ears. The present study was undertaken to investigate the effect of different blanching treatments on peroxidase inactivation, physicochemical properties, and functional properties of baby corn. The treatments applied were hot water blanching (HWB) at temperatures ranging from 70°C to 90 °C for 30-240 s, steam blanching (SB) for 30-240 s, and microwave blanching (MWB) at power levels of 360 W-900 W for 30-300 s. Results indicated that 90 % peroxidase enzyme inactivation occurred under different methods as 90 °C for 60 s for HWB, 100 °C for 60 s for SB, and 540 W for 30 s for MWB. These blanching methods have shown significant effects on the properties under investigation. MWB demonstrated the highest retention of ascorbic acid (94.15 %) and minimal color changes (ΔE = 5.72) in comparison to hot water and steam blanching. Similarly, the result for total flavonoid content for 540 W, 90 °C and 100 °C for 30, 60, and 60 s were found to be 3.01,1.99 and 2.10 mg QE/100g, phenols 48.98, 47.99 and 48.03 mg GAE/100g and DPPH (%) 42.55, 34.20 and 37.08 % respectively. The findings suggest that microwave blanching of baby corn at 540 W for 30 s holds promise to inactivate the peroxidase enzyme with better retention of physicochemical and functional properties.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Baby corn; Blanching; Peroxidase; Physical chemical properties.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Mehan S., Kaur P., Singh M. Studies on effect of storage on quality of minimally processed babycorn. J. Food Process. Technol. 2014 doi: 10.4172/2157-7110.1000388. - DOI
-
- Attia M.M., Saleh S.M.M., El-Shabrawy E.M. Effect of anti-browning agents and wrapping films on browning inhibition and maintaining quality of baby corn during storage. J. Plant Prod. 2011 doi: 10.21608/JPP.2011.85768. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

