Trajectories and influencing factors of psychological resilience among Chinese patients with maintenance hemodialysis
- PMID: 39286215
- PMCID: PMC11403536
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37200
Trajectories and influencing factors of psychological resilience among Chinese patients with maintenance hemodialysis
Abstract
Objective: To identify distinct trajectories of psychological resilience among Chinese patients with maintenance hemodialysis, explore influencing factors and inform the formulation of corresponding interventions.
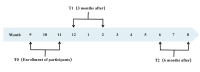
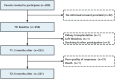
Methods: This was a multi-center longitudinal study with a 6-month follow-up. With convenience sampling, a total of 231 patients with maintenance hemodialysis were recruited between September 2020 and July 2021. Patients' characteristics, including sociodemographic information, social support and family resilience was collected through structured questionnaires as potential baseline influencing factors of psychological resilience trajectories. Psychological resilience was evaluated using the 25-item Chinese version of the Conner and Davidson resilience scale. Latent class growth modeling was conducted to identify homogeneous subgroups with distinct trajectories of psychological resilience. Univariable and multinomial logistic regression analysis were used to examine whether baseline influencing factors were associated with trajectories in patients with maintenance hemodialysis.
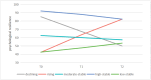
Results: Five distinct psychological resilience trajectory groups were identified: declining group (n = 20, 8.7 %), rising group (n = 17, 7.4 %), moderate-stable group (n = 128, 55.4 %), high-stable group (n = 7, 3.0 %) and low-stable group (n = 59, 25.5 %). High-stable group and moderate-stable group were combined into the well-psychological resilience group for multinomial logistic regression analysis. The multinomial logistic regression analysis showed that influencing factors associated with trajectories of psychological resilience were age, religion, monthly household income per capita, and baseline family resilience.
Conclusions: The results highlight the heterogeneity in the development of psychological resilience among Chinese patients with maintenance hemodialysis. There is a need for healthcare professionals to screen for trajectories of psychological resilience in Chinese maintenance hemodialysis patients and prepare individual mental healthcare interventions.
Keywords: Longitudinal study; Maintenance hemodialysis; Psychological resilience; Trajectory.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Hemodialysis Adequacy Collaborative Group NB Chinese medical doctors' association, China. Clinical practice guidelines for hemodialysis adequacy in China. Chin. J. Med. 2015;34(95):2748–2753. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2015.34.004. - DOI
-
- Yu X., Cao S.M., Ji X.J., Chang M., Xu Jun. The impact of exercise intervention during hemodialysis on patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Nurs. J. 2021;17(36):5–8. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2021.17.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources