Bridging gaps and seeding futures: A synthesis of soil salinization and the role of plant-soil interactions under climate change
- PMID: 39286506
- PMCID: PMC11404172
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110804
Bridging gaps and seeding futures: A synthesis of soil salinization and the role of plant-soil interactions under climate change
Abstract
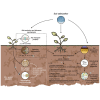
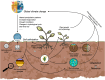
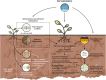
Soil salinization, exacerbated by climate change, poses significant threats to agricultural productivity, land restoration, and ecosystem resilience. This study reviews current knowledge on plant-soil interactions as a strategy to mitigate soil salinization induced by climate change, focusing on their role in soil salinity dynamics and tolerance mechanisms. The review examines how alterations in hydrological and temperature regimes impact soil salinity and how plant-soil mechanisms-such as salt exclusion, compartmentalization, and plant-microbe interactions-contribute to salinity mitigation. This, in turn, enhances soil quality, fertility, microbial diversity, and ecosystem services. The analysis identifies a growing body of research and highlights key themes and emerging trends, including drought, microbial communities, and salt tolerance strategies. This study underscores the critical role of plant-soil interactions in sustainable salinity management and identifies knowledge gaps and future research priorities, advocating for plant-soil interactions as a crucial pathway for improving ecosystem resilience to salinity stress amid climate change.
Keywords: Agricultural science; Agricultural soil science; Soil science.
© 2024 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Machado R., Serralheiro R. Soil salinity: Effect on vegetable crop growth. Management practices to prevent and mitigate soil salinization. Horticulturae. 2017;3:30. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae3020030. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

