Anoikis in cell fate, physiopathology, and therapeutic interventions
- PMID: 39286778
- PMCID: PMC11401975
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.718
Anoikis in cell fate, physiopathology, and therapeutic interventions
Abstract
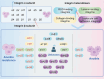
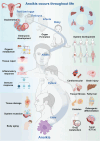
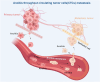
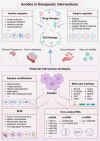
The extracellular matrix (ECM) governs a wide spectrum of cellular fate processes, with a particular emphasis on anoikis, an integrin-dependent form of cell death. Currently, anoikis is defined as an intrinsic apoptosis. In contrast to traditional apoptosis and necroptosis, integrin correlates ECM signaling with intracellular signaling cascades, describing the full process of anoikis. However, anoikis is frequently overlooked in physiological and pathological processes as well as traditional in vitro research models. In this review, we summarized the role of anoikis in physiological and pathological processes, spanning embryonic development, organ development, tissue repair, inflammatory responses, cardiovascular diseases, tumor metastasis, and so on. Similarly, in the realm of stem cell research focused on the functional evolution of cells, anoikis offers a potential solution to various challenges, including in vitro cell culture models, stem cell therapy, cell transplantation, and engineering applications, which are largely based on the regulation of cell fate by anoikis. More importantly, the regulatory mechanisms of anoikis based on molecular processes and ECM signaling will provide new strategies for therapeutic interventions (drug therapy and cell-based therapy) in disease. In summary, this review provides a systematic elaboration of anoikis, thus shedding light on its future research.
Keywords: anoikis; cell death; circulating tumor cells; extracellular matrix; integrin; tumor metastasis.
© 2024 The Author(s). MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Long KR, Newland B, Florio M, et al. Extracellular matrix components hapln1, lumican, and collagen i cause hyaluronic acid‐dependent folding of the developing human neocortex. Neuron. 2018;99(4):702‐719. - PubMed
-
- Bateman JF, Boot‐Handford RP, Lamandé SR. Genetic diseases of connective tissues: cellular and extracellular effects of ecm mutations. Nat Rev Genet. 2009;10(3):173‐183. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
