Research on the soothing Liver - Qi stagnation method in the treatment of postoperative papillary thyroid carcinoma patients' concomitant depression: A randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 39287310
- PMCID: PMC11404975
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039325
Research on the soothing Liver - Qi stagnation method in the treatment of postoperative papillary thyroid carcinoma patients' concomitant depression: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Postoperative papillary thyroid carcinoma (P-PTC) patients often grapple with depression fueled by the looming threat of recurrence. While the Liver-Qi stagnation method is frequently employed for depression management, a notable scarcity of clinical trials exists regarding its application in patients with P-PTC and concurrent depression. This study presents a randomized controlled clinical trial, aiming to establish the efficacy of the Liver-Qi stagnation method in alleviating depression in patients with P-PTC.
Methods: In this randomized controlled clinical trial, P-PTC patients diagnosed with concomitant depression were systematically enrolled. Subjects were randomly assigned to either the control or test group, both receiving standard treatment comprising Levothyroxine sodium tablets and decoction of benefiting Qi and nourishing Yin. Additionally, the test group received supplementation with bupleuri radix-paeoniae alba radix (CH-BS) alongside the baseline therapy. The intervention spanned 12 weeks. Pre- and post-treatment evaluations were conducted using the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD), European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-C30) and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) syndrome score scale. Concurrently, blood inflammatory factors and serum 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) levels were measured to comprehensively assess treatment outcomes.
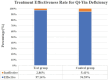
Results: During the 12-week intervention, the test group demonstrated a significant reduction in HAMD scores compared to the control group (P < .05). Moreover, post-treatment serum 5-HT levels were significantly elevated in the test group compared to the control group (P < .05). Findings gleaned from the EORTC QLQ - C30 revealed a noteworthy improvement in social function and overall quality of life scores within both groups post-treatment in comparison to baseline (P < .05). Concurrently, post-treatment scores for fatigue and insomnia symptoms witnessed a significant decrease compared to baseline (P < .05). Notably, the test group exhibited superior scores in the emotional domain in contrast to the control group (P < .05). Both groups exhibited a substantial decrease in TCM syndrome scores from baseline (P < .05). Noteworthy increases were found in IFN-γ < 2.44 rate (62.86%) and IL-6 < 2.44 rate (74.29%) in the test group compared to pretreatment levels (P < .05).
Conclusion: The soothing Liver-Qi stagnation method induces a rise in serum 5-HT levels, reducing depression-related inflammatory factors, culminating in the alleviation of depression for P-PTC.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Helgeson VS, Cohen S, Schulz R, Yasko J. Group support interventions for women with breast cancer: who benefits from what. Health Psychol. 2000;19:107–14. - PubMed
-
- Goswami S, Mongelli M, Peipert BJ, Helenowski I, Yount SE, Sturgeon C. Benchmarking health-related quality of life in thyroid cancer versus other cancers and United States normative data. Surgery. 2018;164:986–92. - PubMed
-
- Hedman C, Strang P, Djärv T, Widberg I, Lundgren CI. Anxiety and fear of recurrence despite a good prognosis: an interview study with differentiated thyroid cancer patients. Thyroid. 2017;27:1417–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous