Real-world efficacy and safety of durvalumab-tremelimumab as second-line systemic therapy after atezolizumab-bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 39288227
- PMCID: PMC11346847
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039289
Real-world efficacy and safety of durvalumab-tremelimumab as second-line systemic therapy after atezolizumab-bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
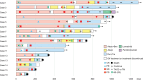
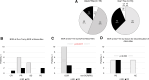
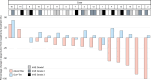
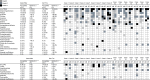
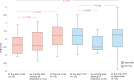
The efficacy and safety of immune-checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma are known. We explored ICI rechallenges with direct switching from 1 ICI regimen to another. This retrospective study included 16 patients who received atezolizumab-bevacizumab (Atezo+Bev) and durvalumab-tremelimumab (Dur+Tre) as the first-line and second-line combination therapy, respectively, at Hiroshima University Hospital. The radiological response and adverse event were evaluated in all patients. Of the 16 patients, 12 were male, and the median age at Atezo+Bev induction was 71 years. The reasons for medication changes were disease progression in 11 patients and adverse events in 5 patients. With Atezo+Bev and Dur+Tre initiation, the Barcelona-Clinic Liver-Cancer stage (A/B/C) progressed in 9/6/3 and 3/4/9 patients and the Child-Pugh classification (A/B/C) progressed in 12/4/0 and 9/6/3 patients, respectively. The disease control rate and overall response rate of Atezo+Bev were 87.5% and 58.3%, respectively, and of Dur+Tre were 62.5% and 0%, respectively. The most common immune-related adverse event in both the Atezo+Bev and Dur+Tre groups was colitis; 3 of the 5 patients with colitis on Atezo+Bev treatment had colitis with Dur+Tre, and 2 had exacerbations. Regarding liver function, ALBI score significantly decreased during Atezo+Bev, but not Dur+Tre, treatment. In patients with colitis following Atezo+Bev, subsequent Dur+Tre treatment may induce colitis recurrence or exacerbation. For immune-related adverse events other than colitis, Dur+Tre could provide relatively safe disease control while maintaining liver function.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 23K07463, Takeda Science Foundation Grant Number 2022043779, 2022 Bristol-Myers Squibb KK Research Grants and by The Hiroshima University Fund “Nozomi H Foundation” subsidy for the promotion of cancer treatment research.TK received honorarium from Astra Zeneca and Chugai Pharma. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. . Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, et al. .; IMbrave150 Investigators. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1894–905. - PubMed
-
- Abou-Alfa GK, Lau G, Kudo M, et al. . Tremelimumab plus durvalumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. NEJM Evid. 2022;1:EVIDoa2100070. - PubMed
-
- Hasegawa K, Takemura N, Yamashita T, et al. .; Committee for Revision of the Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Tokyo, Japan. Clinical practice guidelines for hepatocellular carcinoma: the Japan Society of Hepatology 2021 version (5th JSH-HCC Guidelines). Hepatol Res. 2023;53:383–90. - PubMed
-
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Version 2.2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

