Neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab compared with neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-671): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial
- PMID: 39288781
- PMCID: PMC11512588
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01756-2
Neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab compared with neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone in patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-671): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial
Abstract
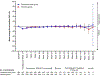
Background: At the first interim analysis of the KEYNOTE-671 trial, adding perioperative pembrolizumab to neoadjuvant chemotherapy significantly improved event-free survival in participants with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We report overall survival and health-related quality of life outcomes from the second interim analysis.
Methods: KEYNOTE-671 was a global phase 3 trial done at 189 medical centres. Eligible participants (aged ≥18 years) with resectable stage II, IIIA, or IIIB (N2) NSCLC were randomly assigned (1:1) to four cycles of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab (200 mg administered intravenously every 3 weeks) plus cisplatin-based chemotherapy followed by surgery and 13 cycles of adjuvant pembrolizumab (200 mg administered intravenously every 3 weeks) or to four cycles of neoadjuvant placebo (administered intravenously every 3 weeks) plus cisplatin-based chemotherapy followed by surgery and 13 cycles of adjuvant placebo (administered intravenously every 3 weeks). Randomisation was done centrally using an interactive response technology system and was stratified by disease stage, PD-L1 expression, histology, and geographical region in blocks of four. Participants, investigators, and sponsor personnel were masked to treatment assignments; local pharmacists were unmasked to support treatment preparation. The dual primary endpoints were overall survival and event-free survival evaluated in the intention-to-treat population. This study is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03425643, and is ongoing but closed to enrolment.
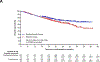
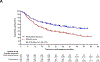
Findings: Between May 11, 2018, and Dec 15, 2021, 797 participants were randomly assigned to the pembrolizumab group (n=397) or the placebo group (n=400). Median study follow-up at the second interim analysis was 36·6 months (IQR 27·6-47·8). 36-month overall survival estimates were 71% (95% CI 66-76) in the pembrolizumab group and 64% (58-69) in the placebo group (hazard ratio 0·72 [95% CI 0·56-0·93]; one-sided p=0·0052; threshold, one-sided p=0·0054). Median event-free survival was 47·2 months (95% CI 32·9 to not reached) in the pembrolizumab group and 18·3 months (14·8-22·1) in the placebo group (hazard ratio 0·59 [95% CI 0·48-0·72]). In the as-treated population, grade 3-5 treatment-related adverse events occurred in 179 (45%) of 396 participants in the pembrolizumab group and in 151 (38%) of 399 participants in the placebo group. Treatment-related adverse events led to death in four (1%) participants in the pembrolizumab group and three (1%) participants in the placebo group.
Interpretation: The significant overall survival benefit of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by adjuvant pembrolizumab compared with neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone coupled with a manageable safety profile support the use of perioperative pembrolizumab in patients with resectable, early-stage NSCLC.
Funding: Merck Sharp & Dohme, a subsidiary of Merck & Co, Rahway, NJ, USA.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests JDS, MCG, HW, ML, TK, MT, S-HL, K-NC, CD, MM, EE, GLM, OB, DR-A, JEC, SN, and SG report funding to their institution from Merck Sharp & Dohme (MSD), a subsidiary of Merck & Co, Rahway, NJ, USA to support conduct of this study. JDS, MCG, HW, ML, TK, MT, S-HL, K-NC, CD, MM, EE, GLM, OB, DR-A, JEC, SN, JY, AA, SMK, AS, and SG received medical writing and editorial support for the preparation of this manuscript from MSD. JDS additionally reports receiving grants to the institution from AstraZeneca, MSD, Roche, BMS, CLS Therapeutics, Protalix Biotherapeutics, Pfizer, and Regeneron; receiving consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Merck, Roche, BMS, Novartis, Chemocentryx, Amgen, Protalix Biotherapeutics, Xenetic Biosciences, Regeneron, Eisai, and Pfizer; receiving payment for a speaking role from Peerview, OncLive, and Medscape; receiving support for attending meetings or travel from AstraZeneca, Merck, and BMS; participating on a clinical trial safety monitoring board for AstraZeneca; and receiving equipment, materials, drugs, gifts, or other services via grant to the institution from Roche, MSD, BMS, and AstraZeneca. MCG additionally reports receiving consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Abion, MSD International, Bayer, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim Italia, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Incyte, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Takeda, Seattle Genetics, Mirati, Daiichi-Sankyo, Regeneron, Merck & Co, Blueprint, Janssen, Sanofi, AbbVie, BeiGene, Oncohost, Medscape, Gilead, Io Biotech, and Revolution Medicines; receiving payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers' bureaus, or educational events from AstraZeneca, Merck & Co, Daiichi Sankyo, Gilead, Eli Lilly, and Regeneron; and receiving support for attending meetings or travel from AstraZeneca. HW additionally reports research funding to the institution from Bayer, AstraZeneca, BMS, Genentech/Roche, MSD, Helsinn, SeaGen, and Xcovery; serving as a compensated advisory board member for Mirati, IOBiotech, OncoC4, and BeiGene; serving as an uncompensated advisory board member for MSD, Genentech/Roche, BMS, and AstraZeneca; serving as a past president of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC); and serving on the executive committee of ECOG-ACRIN. TK additionally reports research grants to the institution from AbbVie, Amgen, Arrivent, AstraZeneca, Bayer, BeiGene, BluePrint, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Haihe, Janssen, Merck KGaA, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, and Takeda; receiving honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers' bureaus, or educational events from Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck KGaA, MSD, Novartis, Ono, Pfizer, Taiho, and Takeda; receiving honoraria for participation on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board from AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Chugai, Daiichi-Sankyo, Janssen, Merck KGaA, MSD, Novartis, and Pfizer; and having a spouse who is an employee of Eli Lilly. MT additionally reports research grants to the institution from MSD, AstraZeneca KK, Bristol-Myers Squibb KK, Ono Pharmaceutical Co, Eli Lilly Japan, Novartis, MiRXES, and Johnson & Johnson Japan; receiving honoraria for lectures from Amgen KK, Johnson & Johnson Japan, Medtronic Japan, AstraZeneca KK, Eli Lilly Japan, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co, Taiho Pharma, Bristol-Myers Squibb KK, Ono Pharmaceutical Co, Novartis, MSD, and Daiichi-Sankyo; serving as a participant on an advisory board for Bristol-Myers Squibb KK, AstraZeneca KK, MSD, Novartis, and MiRXES; and serving as a participant on a data safety monitoring board for Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. S-HL additionally reports research grants to the institution from MSD and receiving honoraria for a lecture from MSD. MM additionally reports receiving honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers' bureaus, or educational events from MSD, Lilly, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Roche, Sanofi, Regeneron, BeiGene, Immedica, Novartis, and BMS; and receiving support to attend meetings or travel from MSD, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Roche. EE additionally reports receiving payment for expert testimony from MSD. OB additionally reports support for attending meetings or travel from MSD for ASCO 2023 and from AstraZeneca for ESMO 2023 and ASCO 2024; and participating as a compensated advisory board member for BMS, Roche, Takeda, MSD, AstraZeneca, Janssen, and MSD. DR-A additionally reports receiving honoraria for lectures from MSD, Roche, BMS, Novartis, Takeda, Lilly, and AstraZeneca; receiving support for attending meetings or travel from Roche, MSD, Novartis, and Sanofi; and participation on an advisory board from MSD, Regeneron, BMS, GSK, and Lilly. JEC additionally reports receiving research grants to the institution from AstraZeneca, BMS, Novartis, Genentech, Merck & Co, and BeiGene; and receiving consulting fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, BMS, Lilly, Genentech, Merck & Co, Regeneron-Sanofi, Janssen, Guardant Health, Flame Biosciences, and Roche. SN additionally reports receiving honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers' bureaus, or educational events from AstraZeneca, Amgen, BeiGene, Pfizer, MSD, Sanofi, Takeda, Thermo Fisher, Janssen, Novartis, and Roche; and participating on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board from AstraZeneca, Amgen, BeiGene, Pfizer, MSD, Sanofi, Takeda, Janssen, and Roche. JY additionally reports receiving salary for full-time employment from MSD. AA, SMK, and AS additionally report receiving salary for full-time employment from MSD and holding stock in Merck & Co, Rahway, NJ, USA.
Figures



Comment in
-
Improved survival for patients with lung cancer treated with perioperative immunotherapy.Lancet. 2024 Sep 28;404(10459):1176-1178. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01920-2. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 39288778 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rosell R, Gomez-Codina J, Camps C, et al. A randomized trial comparing preoperative chemotherapy plus surgery with surgery alone in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 1994; 330: 153–8. - PubMed
-
- Roth JA, Fossella F, Komaki R, et al. A randomized trial comparing perioperative chemotherapy and surgery with surgery alone in resectable stage IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 1994; 86: 673–80. - PubMed
-
- Conroy MR, Dennehy C, Forde PM. Neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2023; 183: 107314. - PubMed
-
- Brierly JD, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. Eighth Edition. Oxford, UK: John Wiley & Sons; 2016.
-
- Tsuboi M, Herbst RS, John T, et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in resected EGFR-mutated NSCLC. N Engl J Med 2023; 389: 137–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

