An object numbering task reveals an underestimation of complexity for typically structured scenes
- PMID: 39289240
- PMCID: PMC12000177
- DOI: 10.3758/s13423-024-02577-2
An object numbering task reveals an underestimation of complexity for typically structured scenes
Abstract
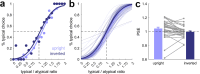
Our visual environments are composed of an abundance of individual objects. The efficiency with which we can parse such rich environments is remarkable. Previous work suggests that this efficiency is partly explained by grouping mechanisms, which allow the visual system to process the objects that surround us as meaningful groups rather than individual entities. Here, we show that the grouping of objects in typically and meaningfully structured environments directly relates to a reduction of perceived complexity. In an object numerosity discrimination task, we showed participants pairs of schematic scene miniatures, in which objects were structured in typical or atypical ways and asked them to judge which scene consisted of more individual objects. Critically, participants underestimated the number of objects in typically structured compared with atypically structured scenes, suggesting that grouping based on typical object configurations reduces the perceived numerical complexity of a scene. In two control experiments, we show that this overestimation also occurs when the objects are presented on textured backgrounds, and that it is specific to upright scenes, indicating that it is not related to basic visual feature differences between typically and atypically structured scenes. Together, our results suggest that our visual surroundings appear less complex to the visual system than the number of objects in them makes us believe.
Keywords: Complexity; Numerosity; Object regularities; Scene perception.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflicts of interest: The authors have no competing interests to declare. Ethics approval: Procedures were approved by the general ethical committee of the Justus Liebig University Gießen. Consent to participate: Each participant provided written informed consent prior to the experiments. Consent for publication: Each participant provided written informed consent to sharing their data publicly in anonymized form.
Figures



References
-
- Biederman, I., Mezzanotte, R. J., & Rabinowitz, J. C. (1982). Scene perception: Detecting and judging objects undergoing relational violations. Cognitive Psychology,14(2), 143–177. - PubMed
-
- Brainard, D. H. (1997). The psychophysics toolbox. Spatial Vision,10(4), 433–436. - PubMed
-
- Chakravarthi, R., Nordqvist, A., Poncet, M., & Adamian, N. (2023). Fundamental units of numerosity estimation. Cognition,239, 105565. - PubMed
-
- Feigenson, L., Dehaene, S., & Spelke, E. (2004). Core systems of number. Trends in Cognitive Sciences,8(7), 307–314. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

