DNA Methylation signatures underpinning blood neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio during first week of human life
- PMID: 39289350
- PMCID: PMC11408723
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-52283-9
DNA Methylation signatures underpinning blood neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio during first week of human life
Abstract
Understanding of newborn immune ontogeny in the first week of life will enable age-appropriate strategies for safeguarding vulnerable newborns against infectious diseases. Here we conducted an observational study exploring the immunological profile of infants longitudinally throughout their first week of life. Our Expanded Program on Immunization - Human Immunology Project Consortium (EPIC-HIPC) studies the epigenetic regulation of systemic immunity using small volumes of peripheral blood samples collected from West African neonates on days of life (DOL) 0, 1, 3, and 7. Genome-wide DNA methylation and single nucleotide polymorphism markers are examined alongside matched transcriptomic and flow cytometric data. Integrative analysis reveals that a core network of transcription factors mediates dynamic shifts in neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratios (NLR), which are underpinned by cell-type specific methylation patterns in the two cell types. Genetic variants are associated with lower NLRs at birth, and healthy newborns with lower NLRs at birth are more likely to subsequently develop sepsis. These findings provide valuable insights into the early-life determinants of immune system development.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
OL is the inventor of patents helped by Boston Children’s Hospital relating to vaccine adjuvants (EP3709998A1) and human in vitro systems that model responses to immunomodulators and vaccines (e.g., US20150152385A1). Hi is an advisor to GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and Hillevax and a cofounder of and advisor to Ovax Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

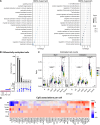

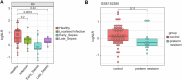
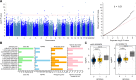
References
-
- Oza, S., Cousens, S. N. & Lawn, J. E. Estimation of daily risk of neonatal death, including the day of birth, in 186 countries in 2013: a vital-registration and modelling-based study. Lancet Glob. Health2, e635–e644 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann-Struzek, C. et al. The global burden of paediatric and neonatal sepsis: a systematic review. Lancet Respir. Med.6, 223–230 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- U19AI118608/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
- K08 AI168487/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI118608/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI168643/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1K08AI168487/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

