Deficiency of Tlr7 and Irf7 in mice increases the severity of COVID-19 through the reduced interferon production
- PMID: 39289468
- PMCID: PMC11408513
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-06872-5
Deficiency of Tlr7 and Irf7 in mice increases the severity of COVID-19 through the reduced interferon production
Abstract
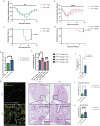
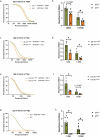
Toll-like receptor 7 (Tlr7) deficiency-accelerated severe COVID-19 is associated with reduced production of interferons (IFNs). However, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. To address these questions, we utilize Tlr7 and Irf7 deficiency mice, single-cell RNA analysis together with bone marrow transplantation approaches. We demonstrate that at the early phase of infection, SARS-CoV-2 causes the upregulation of Tlr7, Irf7, and IFN pathways in the lungs of the infected mice. The deficiency of Tlr7 and Irf7 globally and/or in immune cells in mice increases the severity of COVID-19 via impaired IFN activation in both immune and/or non-immune cells, leading to increased lung viral loads. These effects are associated with reduced IFN alpha and gamma levels in the circulation. The deficiency of Tlr7 tends to cause the reduced production and nuclear translocation of interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) in the lungs of the infected mice, indicative of reduced IRF7 activation. Despite higher amounts of lung viral antigen, Tlr7 or Irf7 deficiency resulted in substantially reduced production of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, thereby delaying the viral clearance. These results highlight the importance of the activation of TLR7 and IRF7 leading to IFN production on the development of innate and adaptive immunity against COVID-19.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R35 HL139930/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK129881/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL165265/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- P51 OD011104/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL165265/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 962950/AHA/American Heart Association-American Stroke Association/United States
- P51OD011104-6/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | NIH Office of the Director (OD)
- R01DK129881/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R21 NR010361/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

