Oxytocin shortens spreading depolarization-induced periorbital allodynia
- PMID: 39289629
- PMCID: PMC11406737
- DOI: 10.1186/s10194-024-01855-7
Oxytocin shortens spreading depolarization-induced periorbital allodynia
Erratum in
-
Correction: Oxytocin shortens spreading depolarization-induced periorbital allodynia.J Headache Pain. 2024 Oct 21;25(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01887-z. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39434018 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Migraine is among the most prevalent and burdensome neurological disorders in the United States based on disability-adjusted life years. Cortical spreading depolarization (SD) is the most likely electrophysiological cause of migraine aura and may be linked to trigeminal nociception. We previously demonstrated, using a minimally invasive optogenetic approach of SD induction (opto-SD), that opto-SD triggers acute periorbital mechanical allodynia that is reversed by 5HT1B/1D receptor agonists, supporting SD-induced activation of migraine-relevant trigeminal pain pathways in mice. Recent data highlight hypothalamic neural circuits in migraine, and SD may activate hypothalamic neurons. Furthermore, neuroanatomical, electrophysiological, and behavioral data suggest a homeostatic analgesic function of hypothalamic neuropeptide hormone, oxytocin. We, therefore, examined the role of hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and oxytocinergic (OXT) signaling in opto-SD-induced trigeminal pain behavior.
Methods: We induced a single opto-SD in adult male and female Thy1-ChR2-YFP transgenic mice and quantified fos immunolabeling in the PVN and supraoptic nucleus (SON) compared with sham controls. Oxytocin expression was also measured in fos-positive neurons in the PVN. Periorbital mechanical allodynia was tested after treatment with selective OXT receptor antagonist L-368,899 (5 to 25 mg/kg i.p.) or vehicle at 1, 2, and 4 h after opto-SD or sham stimulation using von Frey monofilaments.
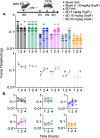
Results: Opto-SD significantly increased the number of fos immunoreactive cells in the PVN and SON as compared to sham stimulation (p < 0.001, p = 0.018, respectively). A subpopulation of fos-positive neurons also stained positive for oxytocin. Opto-SD evoked periorbital mechanical allodynia 1 h after SD (p = 0.001 vs. sham), which recovered quickly within 2 h (p = 0.638). OXT receptor antagonist L-368,899 dose-dependently prolonged SD-induced periorbital allodynia (p < 0.001). L-368,899 did not affect mechanical thresholds in the absence of opto-SD.
Conclusions: These data support an SD-induced activation of PVN neurons and a role for endogenous OXT in alleviating acute SD-induced trigeminal allodynia by shortening its duration.
Keywords: Migraine with aura; Oxytocin; Spreading depolarization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author AH is a member of the Editorial Board of The Journal of Headache and Pain and was not involved in the journal’s peer review process of, or decisions related to, this manuscript. AH is on the Board of Directors of the American Headache Society, American Migraine Foundation and Headache Cooperative of New England, has served on Scientific Advisory Board for Theranica and Abbvie. CA is a Guest Editor of the collection Spreading Depolarization in Headache Disorders and is a member of the Editorial Board of The Journal of Headache and Pain. CA was not involved in the journal’s peer review process of, or decisions related to, this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Rasmussen B.K., Olesen J (1992) Migraine with aura and migraine without aura: an epidemiological study. Cephalalgia. 12(4):221–8 (discussion 186) - PubMed
-
- Viana M et al (2017) Clinical features of migraine aura: Results from a prospective diary-aided study. Cephalalgia 37(10):979–989 - PubMed
-
- Hansen JM, Goadsby PJ, Charles AC (2016) Variability of clinical features in attacks of migraine with aura. Cephalalgia 36(3):216–224 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

