Mortality and functional outcomes 18 months after hospitalization for COVID-19 in geriatric patients: a multicentric cohort study
- PMID: 39289641
- PMCID: PMC11406854
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-024-05240-6
Mortality and functional outcomes 18 months after hospitalization for COVID-19 in geriatric patients: a multicentric cohort study
Abstract
Background: Few data are available on the long-term mortality and functional status of geriatric patients surviving after hospitalization for COVID-19. We compared the mortality and functional status 18 months after hospitalization for geriatric patients who were hospitalized for COVID-19 or another diagnosis.
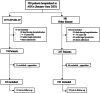
Methods: This was a multicentric cohort study in Paris from January to June 2021. We included patients aged 75 years and over who were hospitalized with COVID-19 or not during this period and compared their vital and functional status 18 months after hospitalization.
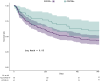
Results: We included 254 patients (63 hospitalized for COVID-19). As compared with patients hospitalized for other reasons, those hospitalized for COVID-19 were younger (mean [SD] age 86 [6.47] vs. 88 [6.41] years, p = 0.03), less frail (median Clinical Frailty Scale score 5 [4-6] vs. 6 [4-6], p 0.007) and more independent at baseline (median activities of daily living score 5.5 [4-6] vs. 5 [3.5-6], p 0.03; instrumental activities of daily living score 3 [1-4] vs. 2 [0-3], p 0.04). At 18 months, 50.8% (n = 32/63) of COVID-19 patients had died versus 66% (n = 126/191) of non-COVID-19 patients (p 0.03). On multivariate analysis, COVID-19 positivity was not significantly associated with 18-month mortality (adjusted hazard ratio 0.67, 95% confidence interval 0.40 to 1.13). At 18 months, the two groups did not differ in activities of daily living or frailty scores.
Conclusions: In this multicenter study of long-term mortality in geriatric patients discharged alive after hospitalization, positive COVID-19 status was not associated with excess mortality.
Keywords: Long-term mortality; Older; Prognosis; SARS-CoV2.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. May 2024. https://covid19.who.int/ Accessed June 1, 2024.
-
- Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, et al. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;324:782–93. 10.1001/jama.2020.12839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous