Exploring the Confluence of Animal Medicine and its Implications for Human Health: A Systematic Literature Review
- PMID: 39289932
- PMCID: PMC12172238
- DOI: 10.2174/011570159X333443240822115028
Exploring the Confluence of Animal Medicine and its Implications for Human Health: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
Introduction: The abuse of veterinary drugs has emerged as a concerning trend, with global fatalities on the rise. Our understanding of this phenomenon remains limited. This study aims to identify the veterinary drugs being misused, the reasons behind their misuse, and how they are obtained.
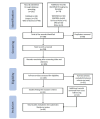
Methods: Utilising PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science databases, along with related grey literature, we applied the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) framework for data collection. Screening and cross-referencing yielded 66 relevant articles, encompassing case reports, surveys, reports, and systemic literature reviews. The analysis identified 28 distinct veterinary drugs being misused in humans, primarily falling into categories, e.g., α-2- and β-2-adrenergic receptor agonists, GABAergic receptor modulators, opioid receptor agonists, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists. These drugs were used for various purposes, including recreational use, weight loss, bodybuilding, pain relief, and self-medication for stress-related symptoms.
Results: Routes of administration predominantly included parenteral, oral, and inhalation methods. Veterinary workers/assistants and individuals connected to animals were identified as contributors to the misuse of these medications. Motivations for their utilisation ranged from affordability and accessibility to the ease of obtaining multiple prescriptions from various veterinary sources, often in conjunction with other illicit substances. Dependence and addiction were common outcomes of the misuse of veterinary medicines by humans.
Conclusion: Overall, this systematic review underscores the increasing popularity of veterinary prescription drug misuse despite being under-reported with limited available data. Healthcare professionals are urged to remain vigilant to potential overdose events involving these medications.
Keywords: Veterinary medicines; animal medicines; diversion of medicines; drug misuse; self-medication.; substance use.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
F.S. was a member of both the UK Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD; 2011-2019) and the EMA Advisory Board (2011-2023; Psychiatry). A.G., J.D., and E.D. declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wilson C. Addiction to prescription drugs is UK 'Public Health Disaster'. 2016. Available from: https://www.newscientist.com/article/2110089-addiction-to-prescription-d...
-
- Prescription Cost Analysis - England - 2022-23. 2023. Available from: https://www.nhsbsa.nhs.uk/statistical-collections/prescription-cost-anal....
-
- Preston M. The rise in prescription drug addiction. 2022. Available from: https://delamere.com/blog/the-rise-in-prescription-drug-addiction.
-
- Deaths related to drug poisoning in England and Wales: 2021 registrations. 2021. Available from: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/birthsdeathsandmarri....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

