Global, regional, and national epidemiology of ischemic stroke from 1990 to 2021
- PMID: 39290044
- PMCID: PMC11555022
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.16481
Global, regional, and national epidemiology of ischemic stroke from 1990 to 2021
Abstract
Background and purpose: This study aims to examine the global, regional, and national burden of ischemic stroke from 1990 to 2021.
Method: We used data from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 database to comprehensively assess ischemic stroke indicators globally, regionally, and in 204 countries, including incidence, deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), estimated annual percentage change (EAPC), and Joinpoint regression analysis.
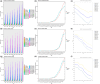
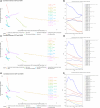
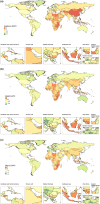
Results: In 2021, there were a total of 7,804,449 cases of ischemic stroke globally (95% uncertainty interval = 6,719,760-8,943,692), with an age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) of 92.39. This represents a declining trend compared to 1990, with an EAPC of -0.67 (95% confidence interval [CI] = -0.76 to -0.58). Mortality and DALY rates also showed a downward trend (EAPC in age-standardized mortality rate: -1.83, 95% CI = -1.92 to -1.74; EAPC in age-standardized DALY rate = -1.59, 95% CI = -1.68 to -1.50). The burden of ischemic stroke was inversely correlated with gross domestic product. Regionally, from 2014 to 2021, the Caribbean experienced the fastest increase in ASIR (annual percent change = 0.15, 95% CI = 0.13 to 0.18). Among 204 countries, North Macedonia had the highest incidence, mortality, and DALY rates. In addition to metabolic risks, particulate matter pollution and low temperatures were significant environmental and occupational risk factors for ischemic stroke. Smoking and a diet high in sodium were identified as key behavioral risk factors.
Conclusions: Ischemic stroke remains a serious global health challenge, and our results from this cross-sectional study suggest that the burden of disease remains high in Eastern Europe, East Asia, Central Asia, and Sub-Saharan Africa.
Keywords: Global Burden of Disease; epidemiology; ischemic stroke; risk factor.
© 2024 The Author(s). European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ji R, Schwamm LH, Pervez MA, Singhal AB. Ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack in young adults: risk factors, diagnostic yield, neuroimaging, and thrombolysis. JAMA Neurol. 2013;70:51‐57. - PubMed
-
- Morotti A, Mazzacane F, Leuci E. Pediatric ischemic stroke. J Neurol. 2020;267:1221‐1222. - PubMed
-
- Bejot Y, Bailly H, Graber M, et al. Impact of the ageing population on the burden of stroke: the Dijon Stroke Registry. Neuroepidemiology. 2019;52:78‐85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Weifang Key Laboratory
- Yuan Du Scholars
- wyfy-2022-ky-148/Clinical Research Center of Affiliated Hospital of Shandong Second Medical University
- LH2022GG03/Joint scientific research plan project of China
- HIGHER2023072/Health China·BuChang ZhiYuan Public welfare projects for heart and brain health under Grant
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

