Discovery of GNE-6893, a Potent, Selective, Orally Bioavailable Small Molecule Inhibitor of HPK1
- PMID: 39291002
- PMCID: PMC11403726
- DOI: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00319
Discovery of GNE-6893, a Potent, Selective, Orally Bioavailable Small Molecule Inhibitor of HPK1
Abstract
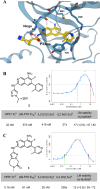
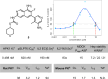
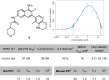
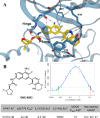
Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (HPK1) serves a key immunosuppressive role as a negative regulator of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling. HPK1 loss-of-function is associated with augmentation of immune function and has demonstrated synergy with immune checkpoint inhibitors in syngeneic mouse cancer models. These data offer compelling evidence for the use of selective small molecule inhibitors of HPK1 in cancer immunotherapy. We identified a novel series of isoquinoline HPK1 inhibitors through fragment-based screening that displayed promising levels of biochemical potency and activity in functional cell-based assays. We used structure-based drug design to introduce key selectivity elements while simultaneously addressing pharmacokinetic liabilities. These efforts culminated in a molecule demonstrating subnanomolar biochemical inhibition of HPK1 and strong in vitro augmentation of TCR signaling in primary human T-cells. Further profiling of this molecule revealed excellent kinase selectivity (347/356 kinases <50% inhibition @ 0.1 μM), a favorable in vitro safety profile, and good projected human pharmacokinetics.
© 2024 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Chen D. S.; Mellman I. Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.012. - DOI - PubMed
- Barbee M. S.; Ogunniyi A.; Horvat T. Z.; Dang T.-O. Current status and future directions of the immune checkpoint inhibitors ipilimumab, pembrolizumab, and nivolumab in oncology. Ann. Pharmacother. 2015, 49, 907–937. 10.1177/1060028015586218. - DOI - PubMed
- Sharma P.; Allison J. P. Immune checkpoint targeting in cancer therapy: toward combination strategies with curative potential. Cell 2015, 161, 205–214. 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mahoney K. M.; Rennert P. D.; Freeman G. J. Combination cancer immunotherapy and new immunomodulatory targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2015, 14, 561–584. 10.1038/nrd4591. - DOI - PubMed
- Heffron T. P.; Chan B. K. Small molecules for cancer immunotherapy. Med. Chem. Rev. 2017, 52, 221–241. 10.29200/acsmedchemrev-v52.ch12. - DOI
-
- Hu M. C.; Qiu W. R.; Wang X.; Meyer C. F.; Tan T. H. Human HPK1, a novel human hematopoietic progenitor kinase that activates the JNK/SAPK kinase cascade. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 2251–2264. 10.1101/gad.10.18.2251. - DOI - PubMed
- Sawasdikosol S.; Burakoff S. A perspective on HPK1 as a novel immuno-oncology drug target. Elife 2020, 9, e55122 10.7554/eLife.55122. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hernandez S.; Qing J.; Thibodeau R. H.; Du X.; Park S.; Lee H.-M.; Xu M.; Oh S.; Navarro A.; Roose-Girma M.; Newman R. J.; Warming S.; Nannini M.; Sampath D.; Kim J. M.; Grogan J. L.; Mellman I. The kinase activity of Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase 1 is essential for the regulation of T cell function. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 80–94. 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.09.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen H.; Guan X.; He C.; Lu T.; Lin X.; Liao X. Current strategies for targeting HPK1 in cancer and the barriers to preclinical progress. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2024, 28, 237–250. 10.1080/14728222.2024.2344697. - DOI - PubMed
- Vara B. A.; Levi S. M.; Achab A.; Candito D. A.; Fradera X.; Lesburg C. A.; Kawamura S.; Lacey B. M.; Lim J.; Methot J. L.; Xu Z.; Xu H.; Smith D. M.; Piesvaux J. A.; Miller J. R.; Bittinger M.; Ranganath S. H.; Bennett D. J.; DiMauro E. F.; Pasternak A. Discovery of Diaminopyrimidine Carboxamide HPK1 Inhibitors as Preclinical Immunotherapy Tool Compounds. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 653–661. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.1c00096. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Yu E. C.; Methot J. L.; Fradera X.; Lesburg C. A.; Lacey B. M.; Siliphaivanh P.; Liu P.; Smith D. M.; Xu Z.; Piesvaux J. A.; Kawamura S.; Xu H.; Miller J. R.; Bittinger M.; Pasternak A. Identification of Potent Reverse Indazole Inhibitors for HPK1. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 459–466. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00672. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Sokolsky A.; Vechorkin O.; Hummel J. R.; Styduhar E. D.; Wang A.; Nguyen M. H.; Ye H. F.; Liu K.; Zhang K.; Pan J.; Ye Q.; Atasoylu O.; Behshad E.; He X.; Conlen P.; Stump K.; Ye M.; Diamond S.; Covington M.; Yeleswaram S.; Yao W. Potent and Selective Biaryl Amide Inhibitors of Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase 1 (HPK1). ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 116–112. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00241. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Wang M. S.; Wang Z. Z.; Li Z. L.; Gong Y.; Duan C. X.; Cheng Q. H.; Huang W.; Yang G. F. Discovery of Macrocycle-based HPK1 Inhibitors for T-Cell-based Immunotherapy. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 611–626. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01551. - DOI - PubMed
- Ye Q.; Liu K.; Ye H.; Pan J.; Sokolsky A.; Wang A.; Zhang K.; Hummel J. R.; Kong L.; Behshad E.; He X.; Conlen P.; Stump K.; Ye M.; Diamond S.; Covington M.; Yeleswaram S.; Atasoylu O.; Vechorkin O.; Yao W. Discovery of Pyrazolopyridine Derivatives as HPK1 Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 5–10. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00238. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Zhu Q.; Chen N.; Tian X.; Zhou Y.; You Q.; Xu X. Hematopoietic Progenitor Kinase 1 in Tumor Immunology: A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8065–8090. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00172. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

