The Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in CKD-Related Vascular Calcification: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics
- PMID: 39291213
- PMCID: PMC11403042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.05.005
The Role of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in CKD-Related Vascular Calcification: From Mechanisms to Therapeutics
Abstract
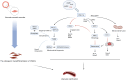
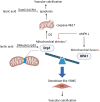
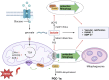
Vascular calcification (VC) is a common complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is closely associated with cardiovascular events. The transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscles (VSMCs) into an osteogenic phenotype is hypothesized to be the primary cause underlying VC. However, there is currently no effective clinical treatment for VC. Growing evidence suggests that mitochondrial dysfunction accelerates the osteogenic differentiation of VSMCs and VC via multiple mechanisms. Therefore, elucidating the relationship between the osteogenic differentiation of VSMCs and mitochondrial dysfunction may assist in improving VC-related adverse clinical outcomes in patients with CKD. This review aimed to summarize the role of mitochondrial biogenesis, mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy, and metabolic reprogramming, as well as mitochondria-associated oxidative stress (OS) and senescence in VC in patients with CKD to offer valuable insights into the clinical treatment of VC.
Keywords: CKD; mitochondria; osteogenic transdifferentiation; vascular calcification; vascular smooth muscle cell.
© 2024 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Bone-Vascular Axis: A Key Player in Chronic Kidney Disease Associated Vascular Calcification.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2024 Sep 6;10(6):545-557. doi: 10.1159/000541280. eCollection 2024 Dec. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39664335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phenotypic plasticity of vascular smooth muscle cells in vascular calcification: Role of mitochondria.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 12;9:972836. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.972836. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36312244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C5a-C5aR1 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress to accelerate vascular calcification via PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CREB3L1 pathway.Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Nov 25;119(15):2563-2578. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad133. Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 37603848
-
Irisin alleviates vascular calcification by inhibiting VSMC osteoblastic transformation and mitochondria dysfunction via AMPK/Drp1 signaling pathway in chronic kidney disease.Atherosclerosis. 2022 Apr;346:36-45. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2022.02.007. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Atherosclerosis. 2022. PMID: 35255258
-
Ubiquitin-specific protease 47 is associated with vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease by regulating osteogenic transdifferentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):752-766. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2072337. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 35509185 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mitochondria‑derived peptides: Promising microproteins in cardiovascular diseases (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2025 May;31(5):127. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13492. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40084698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: The Nexus of Aging, Dyslipidemia, and CKD.Kidney Int Rep. 2025 Jan 10;10(3):973-974. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2025.01.010. eCollection 2025 Mar. Kidney Int Rep. 2025. PMID: 40225394 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Advancing Understanding of Mitochondrial Function in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Dec 5;10(2):285-286. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.12.001. eCollection 2025 Feb. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39990914 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

