Enhanced lipid metabolism reprogramming in CHF rats through IL-6-mediated cardiac glial cell modulation by digilanid C and electroacupuncture stimulation combination
- PMID: 39291267
- PMCID: PMC11405320
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1424395
Enhanced lipid metabolism reprogramming in CHF rats through IL-6-mediated cardiac glial cell modulation by digilanid C and electroacupuncture stimulation combination
Abstract
Background: Cardiac lipid metabolism reprogramming is recognized as a critical pathological factor in the progression of chronic heart failure (CHF). The therapeutic potential of digilanid C and electroacupuncture stimulation (ES) in enhancing lipid metabolism and cardiac function has been established. However, the optimal synergistic regulatory strategies of these interventions on cardiac lipid metabolism have yet to be elucidated.
Methods: This study aimed to comprehensively evaluate the impact of a digilanid C-ES combination on cardiac steatosis remodeling in CHF. Assessments were conducted across various dimensions, including myocardial oxygen consumption, mitochondrial function, and lipid metabolism. Additionally, we sought to uncover the underlying neuromolecular mechanisms.
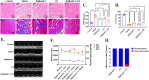
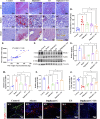
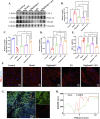
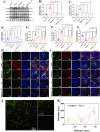
Results: Our findings, at both molecular and morphological levels, indicated that the synergistic application of digilanid C and ES significantly inhibited myocardial fibrosis and steatosis. This combination therapy facilitated the repair of cardiac neuro-vascular uncoupling and induced a reprogramming of lipid metabolism. Notably, the digilanid C-ES combination ameliorated cardiomyocyte apoptosis and enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis in CHF, leading to a restructured energy supply pattern. Cardiac immunofluorescence analyses revealed the aggregation of cardiac glial cells (CGCs) at sites of abnormal neurovascular coupling, a response to cardiac lipid degeneration. This was accompanied by a marked reduction in the abnormally elevated expression of interleukin 6 (IL-6) and glutamatergic signaling, which correlated with the severity of cardiac steatosis and the aberrant activation of CGCs. The combined therapy was found to activate the Janus kinase 1 (JAK1)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway, effectively attenuated lipid accumulation and over-recruitment of CGCs and deprivation of glutamatergic nerves.
Conclusion: These findings underscore the potential of digilanid C and ES combination therapy as a novel approach to modulate the complex interplay between neurovascular dynamics and metabolic dysregulation in CHF.
Keywords: cardiac glial cells; chronic heart failure; digilanid C-electroacupuncture stimulation; glutamatergic; lipid.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Sun, Yuan, Yu, Hou, Jia, Xu and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fysekidis M., Kesse-Guyot E., Valensi P., Arnault N., Galan P., Hercberg S., et al. (2019). Association between adherence to the French dietary guidelines and lower resting heart rate, longer diastole duration, and lower myocardial oxygen consumption. The nutrivasc study. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 15, 463–475. 10.2147/VHRM.S215795 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

