Automated brain segmentation and volumetry in dementia diagnostics: a narrative review with emphasis on FreeSurfer
- PMID: 39291276
- PMCID: PMC11405240
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1459652
Automated brain segmentation and volumetry in dementia diagnostics: a narrative review with emphasis on FreeSurfer
Abstract
Background: Dementia can be caused by numerous different diseases that present variable clinical courses and reveal multiple patterns of brain atrophy, making its accurate early diagnosis by conventional examinative means challenging. Although highly accurate and powerful, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) currently plays only a supportive role in dementia diagnosis, largely due to the enormous volume and diversity of data it generates. AI-based software solutions/algorithms that can perform automated segmentation and volumetry analyses of MRI data are being increasingly used to address this issue. Numerous commercial and non-commercial software solutions for automated brain segmentation and volumetry exist, with FreeSurfer being the most frequently used.
Objectives: This Review is an account of the current situation regarding the application of automated brain segmentation and volumetry to dementia diagnosis.
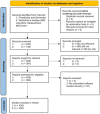
Methods: We performed a PubMed search for “FreeSurfer AND Dementia” and obtained 493 results. Based on these search results, we conducted an in-depth source analysis to identify additional publications, software tools, and methods. Studies were analyzed for design, patient collective, and for statistical evaluation (mathematical methods, correlations).
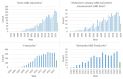
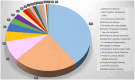
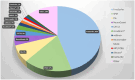
Results: In the studies identified, the main diseases and cohorts represented were Alzheimer’s disease (n = 276), mild cognitive impairment (n = 157), frontotemporal dementia (n = 34), Parkinson’s disease (n = 29), dementia with Lewy bodies (n = 20), and healthy controls (n = 356). The findings and methods of a selection of the studies identified were summarized and discussed.
Conclusion: Our evaluation showed that, while a large number of studies and software solutions are available, many diseases are underrepresented in terms of their incidence. There is therefore plenty of scope for targeted research.
Keywords: FreeSurfer; dementia; review; segmentation; volumetry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Practical methods for segmentation and calculation of brain volume and intracranial volume: a guide and comparison.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022 Jul;12(7):3748-3761. doi: 10.21037/qims-21-958. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022. PMID: 35782251 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-scanner reproducibility of brain volumetry: influence of automated brain segmentation software.BMC Neurosci. 2020 Sep 4;21(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12868-020-00585-1. BMC Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32887546 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of automated brain segmentation using a brain phantom and patients with early Alzheimer's dementia or mild cognitive impairment.Psychiatry Res. 2015 Sep 30;233(3):299-305. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2015.07.011. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Psychiatry Res. 2015. PMID: 26211622
-
Agreement Between Automated and Manual MRI Volumetry in Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022 Aug;56(2):490-507. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28037. Epub 2021 Dec 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2022. PMID: 34964531
-
Liver segmentation: indications, techniques and future directions.Insights Imaging. 2017 Aug;8(4):377-392. doi: 10.1007/s13244-017-0558-1. Epub 2017 Jun 14. Insights Imaging. 2017. PMID: 28616760 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The diagnostic accuracy of CTseg segmentation software for dementia in a New Zealand memory service.J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025 May 21;9:25424823251332448. doi: 10.1177/25424823251332448. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. J Alzheimers Dis Rep. 2025. PMID: 40406677 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Volume Loss After Stereotactic Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy in Patients With Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.J Neuroimaging. 2025 Mar-Apr;35(2):e70039. doi: 10.1111/jon.70039. J Neuroimaging. 2025. PMID: 40197718 Free PMC article.
-
Scan-rescan reliability assessment of brain volumetric analysis across scanners and software solutions.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 14;15(1):29843. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15283-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40813790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailly M., Destrieux C., Hommet C., Mondon K., Cottier J.-P., Beaufils E., et al. . (2015). Precuneus and cingulate cortex atrophy and Hypometabolism in patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and mild cognitive impairment: MRI and 18 F-FDG PET quantitative analysis using FreeSurfer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 1–8. doi: 10.1155/2015/583931, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

