Exercise Alleviates Cardiovascular Diseases by Improving Mitochondrial Homeostasis
- PMID: 39291488
- PMCID: PMC11681480
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.036555
Exercise Alleviates Cardiovascular Diseases by Improving Mitochondrial Homeostasis
Abstract
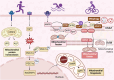
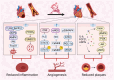
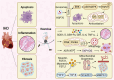
Engaging in regular exercise and physical activity contributes to delaying the onset of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). However, the physiological mechanisms underlying the benefits of regular exercise or physical activity in CVDs remain unclear. The disruption of mitochondrial homeostasis is implicated in the pathological process of CVDs. Exercise training effectively delays the onset and progression of CVDs by significantly ameliorating the disruption of mitochondrial homeostasis. This includes improving mitochondrial biogenesis, increasing mitochondrial fusion, decreasing mitochondrial fission, promoting mitophagy, and mitigating mitochondrial morphology and function. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the benefits of physical exercise in the context of CVDs, establishing a connection between the disruption of mitochondrial homeostasis and the onset of these conditions. Through a detailed examination of the underlying molecular mechanisms within mitochondria, the study illuminates how exercise can provide innovative perspectives for future therapies for CVDs.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; exercise; exerkines; mitochondrial homeostasis.
Figures


References
-
- Kokkinos P, Faselis C, Samuel IBH, Lavie CJ, Zhang J, Vargas JD, Pittaras A, Doumas M, Karasik P, Moore H, et al. Changes in cardiorespiratory fitness and survival in patients with or without cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023;81:1137–1147. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.01.027 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

