Roflumilast Cream, 0.15%, for Atopic Dermatitis in Adults and Children: INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 Randomized Clinical Trials
- PMID: 39292443
- PMCID: PMC11411450
- DOI: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.3121
Roflumilast Cream, 0.15%, for Atopic Dermatitis in Adults and Children: INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2 Randomized Clinical Trials
Erratum in
-
Error in Supplement 2.JAMA Dermatol. 2025 Jun 1;161(6):669-670. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2025.1153. JAMA Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40266584 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Safe, effective, and well-tolerated topical treatment options available for long-term use in patients with atopic dermatitis (AD) are limited and associated with low adherence rates.
Objective: To evaluate efficacy and safety of once-daily roflumilast cream, 0.15%, vs vehicle cream in patients with AD.
Design, setting, and participants: Two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials (Interventional Trial Evaluating Roflumilast Cream for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis 1 and 2 [INTEGUMENT-1 and INTEGUMENT-2]), included patients from sites in the US, Canada, and Poland. Participants were 6 years or older with mild to moderate AD based on Validated Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis (assessed on a 5-point scale ranging from 0 [clear] to 4 [severe]).
Intervention: Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive roflumilast cream, 0.15%, or vehicle cream once daily for 4 weeks.
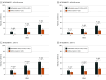
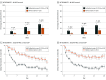
Main outcomes and measures: The primary efficacy end point was Validated Investigator Global Assessment for Atopic Dermatitis success at week 4, defined as a score of 0 or 1 plus at least a 2-grade improvement from baseline. Secondary end points included Eczema Area and Severity Index and Worst Itch Numeric Rating Scale. Safety and local tolerability were also evaluated.
Results: Among 1337 patients (654 patients in INTEGUMENT-1 and 683 patients in INTEGUMENT-2), the mean (SD) age was 27.7 (19.2) years, and 761 participants (56.9%) were female. The mean body surface area involved was 13.6% (SD = 11.6%; range, 3.0% to 88.0%). Significantly more patients treated with roflumilast than vehicle achieved the primary end point (INTEGUMENT-1: 32.0% vs 15.2%, respectively; P < .001; INTEGUMENT-2: 28.9% vs 12.0%, respectively; P < .001). At week 4, statistically significant differences favoring roflumilast also occurred for the achievement of at least 75% reduction in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (INTEGUMENT-1: 43.2% vs 22.0%, respectively; P < .001; INTEGUMENT-2: 42.0% vs 19.7%, respectively; P < .001). Roflumilast was well tolerated with low rates of treatment-emergent adverse events. At each time point, investigators noted no signs of irritation at the application site in 885 patients who were treated with roflumilast (≥95%), and 885 patients who were treated with roflumilast (90%) reported no or mild sensation at the application site.
Conclusions and relevance: In 2 phase 3 trials enrolling adults and children, once-daily roflumilast cream, 0.15%, improved AD relative to vehicle cream, based on multiple efficacy end points, with favorable safety and tolerability.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifiers: NCT04773587, NCT04773600.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Asher MI, Montefort S, Björkstén B, et al. ; ISAAC Phase Three Study Group . Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC phases one and three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet. 2006;368(9537):733-743. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69283-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

