A brain microbiome in salmonids at homeostasis
- PMID: 39292785
- PMCID: PMC11409976
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ado0277
A brain microbiome in salmonids at homeostasis
Abstract
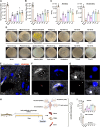
Ectotherms have peculiar relationships with microorganisms. For instance, bacteria are recovered from the blood and internal organs of healthy teleosts. However, the presence of microbial communities in the healthy teleost brain has not been proposed. Here, we report a living bacterial community in the brain of healthy salmonids with bacterial loads comparable to those of the spleen and 1000-fold lower than in the gut. Brain bacterial communities share >50% of their diversity with gut and blood bacterial communities. Using culturomics, we obtained 54 bacterial isolates from the brains of healthy trout. Comparative genomics suggests that brain bacteria may have adaptations for niche colonization and polyamine biosynthesis. In a natural system, Chinook salmon brain microbiomes shift from juveniles to reproductively mature adults. Our study redefines the physiological relationships between the brain and bacteria in teleosts. This symbiosis may endow salmonids with a direct mechanism to sense and respond to environmental microbes.
Figures




References
-
- Cryan J. F., O’Riordan K. J., Cowan C. S., Sandhu K. V., Bastiaanssen T. F., Boehme M., Codagnone M. G., Cussotto S., Fulling C., Golubeva A. V., The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol. Rev. 99, 1877–2013 (2019). - PubMed
-
- O’Riordan K. J., Collins M. K., Moloney G. M., Knox E. G., Aburto M. R., Fülling C., Morley S. J., Clarke G., Schellekens H., Cryan J. F., Short chain fatty acids: Microbial metabolites for gut-brain axis signalling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 546, 111572 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Mohanta L., Das B. C., Patri M., Microbial communities modulating brain functioning and behaviors in zebrafish: A mechanistic approach. Microb. Pathog. 145, 104251 (2020). - PubMed
-
- R. D. Berg, Translocation of indigenous bacteria from the intestinal tract, in Human Intestinal Microflora in Health and Disease (Academic Press, 1983), chap. 15, pp. 333–352.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

