A deep intronic splice-altering AIRE variant causes APECED syndrome through antisense oligonucleotide-targetable pseudoexon inclusion
- PMID: 39292801
- PMCID: PMC12038428
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adk0845
A deep intronic splice-altering AIRE variant causes APECED syndrome through antisense oligonucleotide-targetable pseudoexon inclusion
Abstract
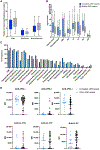
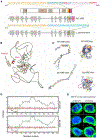
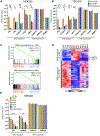
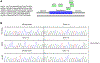
Autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy (APECED) is a life-threatening monogenic autoimmune disorder primarily caused by biallelic deleterious variants in the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene. We prospectively evaluated 104 patients with clinically diagnosed APECED syndrome and identified 17 patients (16%) from 14 kindreds lacking biallelic AIRE variants in exons or flanking intronic regions; 15 had Puerto Rican ancestry. Through whole-genome sequencing, we identified a deep intronic AIRE variant (c.1504-818 G>A) cosegregating with the disease in all 17 patients. We developed a culture system of AIRE-expressing primary patient monocyte-derived dendritic cells and demonstrated that c.1504-818 G>A creates a cryptic splice site and activates inclusion of a 109-base pair frame-shifting pseudoexon. We also found low-level AIRE expression in patient-derived lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) and confirmed pseudoexon inclusion in independent extrathymic AIRE-expressing cell lines. Through protein modeling and transcriptomic analyses of AIRE-transfected human embryonic kidney 293 and thymic epithelial cell 4D6 cells, we showed that this variant alters the carboxyl terminus of the AIRE protein, abrogating its function. Last, we developed an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) that reversed pseudoexon inclusion and restored the normal AIRE transcript sequence in LCLs. Thus, our findings revealed c.1504-818 G>A as a founder APECED-causing AIRE variant in the Puerto Rican population and uncovered pseudoexon inclusion as an ASO-reversible genetic mechanism underlying APECED.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Anderson MS, Venanzi ES, Klein L, Chen Z, Berzins SP, Turley SJ, von Boehmer H, Bronson R, Dierich A, Benoist C, Mathis D, Projection of an immunological self shadow within the thymus by the aire protein. Science 298, 1395–1401 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Oftedal BE, Hellesen A, Erichsen MM, Bratland E, Vardi A, Perheentupa J, Kemp EH, Fiskerstrand T, Viken MK, Weetman AP, Fleishman SJ, Banka S, Newman WG, Sewell WA, Sozaeva LS, Zayats T, Haugarvoll K, Orlova EM, Haavik J, Johansson S, Knappskog PM, Lovas K, Wolff AS, Abramson J, Husebye ES, Dominant mutations in the autoimmune regulator AIRE are associated with common organ-specific autoimmune diseases. Immunity 42, 1185–1196 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Sansom SN, Shikama-Dorn N, Zhanybekova S, Nusspaumer G, Macaulay IC, Deadman ME, Heger A, Ponting CP, Hollander GA, Population and single-cell genomics reveal the Aire dependency, relief from Polycomb silencing, and distribution of self-antigen expression in thymic epithelia. Genome Res. 24, 1918–1931 (2014). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

