Magrolimab plus rituximab with or without chemotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 39293083
- PMCID: PMC11609519
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2024013338
Magrolimab plus rituximab with or without chemotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
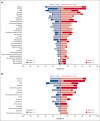
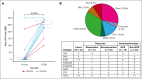
Patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) ineligible for available salvage therapies have limited options for long-term disease control, necessitating novel treatments. Previously, magrolimab (anti-cluster-of-differentiation-47 antibody) plus rituximab (M+R) demonstrated ability to induce complete responses (CR) in R/R DLBCL. Here, we report 3-year follow-up data from this phase 1b/2 study assessing long-term safety and efficacy of M+R, and initial safety and efficacy of M+R plus gemcitabine-oxaliplatin (M+R-GemOx), in R/R DLBCL. After magrolimab priming, 4 groups of patients received M+R, 10 to 45 mg/kg magrolimab with 375 mg/m2 rituximab; patients receiving M+R-GemOx received 30 or 45 mg/kg magrolimab with 375 mg/m2 rituximab, 1000 mg/m2 gemcitabine, and 100 mg/m2 oxaliplatin. Primary end points were treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and objective response rate (ORR). Secondary end points included duration of response (DOR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS). Of 132 patients treated, 99 received M+R and 33 received M+R-GemOx. Most common any-grade TEAEs were fatigue (M+R, 40%; M+R-GemOx, 70%), infusion-related reactions (M+R, 39%), or anemia (M+R-GemOx, 70%). Treatment-related TEAEs led to magrolimab discontinuation in 7% (M+R) and 6% (M+R-GemOx). One death was considered treatment related (M+R-GemOx, colitis). M+R ORR was 24% (CR, 12%), and median DOR was 9.3 months. Median PFS and OS were 1.8 and 9.2 months, respectively. M+R-GemOx ORR was 52% (CR, 39%); 12-month DOR rate was 66.6% (95% confidence interval, 33.1-86.1). Median PFS and OS were 3.9 months and not reached, respectively. These results demonstrate that M+R with/without GemOx is well tolerated, and M+R-GemOx has clinical activity in patients with R/R DLBCL. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02953509.
Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.E.M.’s institution has received research funding on his behalf from Gilead Sciences, Inc, Atara Bio, CRISPR Therapeutics, Precision Biosciences, and Scripps Research Institute. A.A.’s institution has received research funding on his behalf from Forty Seven and Gilead Sciences, Inc. L.P. has received honoraria from Pfizer and Roche, and has received travel, accommodations, and/or expenses from Novartis. G.P.C. has received honoraria for speaker or consultancy work from Roche, Takeda, Kite Pharma/Gilead Sciences, Incyte, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Novartis, SecuraBio, and AbbVie, and research funding from Pfizer, BeiGene, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Inc, and Bristol Myers Squibb. I.W.F. reports consultancy for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Century Therapeutics, Genentech, Inc, Genmab, Hutchison MediPharma, Iksuda Therapeutics, InnoCare Pharma, Janssen, Kite Pharma, MorphoSys, Myeloid Therapeutics, Novartis, Nurix Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Secura Bio, Servier Pharmaceuticals, Takeda, TG Therapeutics, Verastem, Vincerx Pharma, and Xencor, and institutional research grants from AbbVie, Acerta Pharma, Agios, ArQule, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, Biopath, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calibr, Cancer and Leukemia Group B, Celgene, City of Hope National Medical Center, Constellation Pharmaceuticals, Curis, CTI Biopharma, Epizyme, Fate Therapeutics, Forma Therapeutics, Forty Seven, Genentech, Inc, Gilead Sciences, Inc, InnoCare Pharma, IGM Biosciences, Incyte, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Kite Pharma, Loxo, Merck, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, MorphoSys, Myeloid Therapeutics, Novartis, Nurix, Pfizer, Pharmacyclics, Portola Pharmaceuticals, Rhizen Pharmaceuticals, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Seattle Genetics, Tessa Therapeutics, TCR2 Therapeutics, TG Therapeutics, Trillium Therapeutics, Triphase Research and Development Corp, Unum Therapeutics, and Verastem. N.G. has received consulting fees from Seagen, TG Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Pharmacyclics, Janssen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Inc, Kite Pharma, Syncopation, Lava Therapeutics, BeiGene, Incyte, Karyopharm, Roche/Genentech, Inc, Novartis, Loxo Oncology, Genmab, Adaptive Biotech, and ADC Therapeutics; previously served on speakers' bureaus for Gilead Sciences, Inc, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Phamacyclics, Janssen, and Epizyme; and received research funding from TG Therapeutics, Roche/Genentech, Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead Sciences, Inc, MorphoSys, and AbbVie. C.K. has received honoraria from Roche, Gilead Sciences, Inc, Merck Sharp and Dohme, AstraZeneca, Takeda, BeiGene, and Bristol Myer Squibb. M.K. has received consultancy fees from Roche, Antegene, and Genor Biopharm. A.M. has received research funding from Incyte Corp, Takeda, Forty Seven/Gilead Sciences, Juno Pharmaceuticals/Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene/Bristol Myers Squibb, Innate Pharmaceuticals, Seattle Genetics, TG Therapeutics, Affimed, Merck, Kite Pharma/Gilead Sciences, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd/Genentech, Inc, and ADC Therapeutics; consulting fees from Gilead Sciences, Inc, Seattle Genetics, Incyte Corp, MorphoSys, TG Therapeutics, Kyowa Kirin, BeiGene, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd/Genentech, Inc, and ADC Therapeutics; and served on the speakers' bureaus for Incyte Corp/MorphoSys, BeiGene, Ipsen, and Kyowa Kirin. G.H.K. and Y.H. are employed by Gilead Sciences, Inc, and hold stock in Gilead Sciences, Inc. Y.Z. is employed by Gilead Sciences, Inc, and holds stock in Gilead Sciences, Inc, and Allogene Therapeutics, Inc. C.R. was employed by Gilead Sciences, Inc, at the time of the study and held stock in Gilead Sciences, Inc, and Alphabet Inc, Class A. S.M.S. reports consultancy for MorphoSys/Incyte, Janssen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Karyopharm, TG Therapeutics, and Celgene, and received research funding from FortySeven, TG Therapeutics, Pharmacyclics, Acerta, Karyopharm, Portola, Celgene, Novartis, Roche/Genentech, and Epizyme. R.A. has received research funding from BeiGene, Merck, Roche/Genentech, Inc, Seattle Genetics, ADC Therapeutics, Phamacyclics, Cyteir, and Daiichi Sankyo, and has served on advisory boards for Roche/Genentech, MorphoSys, and Epizyme. M.R. declares no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Al-Hamadani M, Habermann TM, Cerhan JR, Macon WR, Maurer MJ, Go RS. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtype distribution, geodemographic patterns, and survival in the US: a longitudinal analysis of the National Cancer Data Base from 1998 to 2011. Am J Hematol. 2015;90(9):790–795. - PubMed
-
- Corazzelli G, Capobianco G, Arcamone M, et al. Long-term results of gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin with and without rituximab as salvage treatment for transplant-ineligible patients with refractory/relapsing B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2009;64(5):907–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

