Comparison of Water Sorption and Water Solubility Properties of Current Restorative Materials with Different Contents
- PMID: 39293490
- PMCID: PMC11750316
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0044-1789270
Comparison of Water Sorption and Water Solubility Properties of Current Restorative Materials with Different Contents
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate and compare water sorption and solubility properties of current restorative materials with different contents.
Materials and methods: Alkasite, self-adhesive restorative material (Cention N, Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein), bulk-fill glass hybrid restorative material (EQUIA Forte HT, GC Corp., Tokyo, Japan), nanohybrid universal composite material (OptiShade, Kerr Dental, United States), and bulk-fill composite material (Filtek One Bulk Fill Restorative, 3M ESPE, St. Paul, Minnesota, United States) were used. Samples (n = 6) were prepared (2 × 10 mm) according to the ISO 4049 standards. Water sorption and solubility values were calculated according to the ISO 4049 standards.
Statistical analysis: One-way ANOVA, Tukey's post-hoc, Tamhane's T2 post-hoc, Pearson's correlation, and independent samples t-tests were used for statistical analysis (p < 0.05).
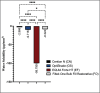
Results: Group EQUIA Forte HT significantly showed the highest water sorption values (57.278 ± 3.174), while Group Filtek One Bulk Fill Restorative exhibited the lowest (4.429 ± 0.174; p < 0.05). The water sorption values for Group Cention N were 5.000 ± 0.542. Group EQUIA Forte HT significantly had the lowest water solubility values (-99.799 ± 1.909), while Group Cention N (-2.966 ± 0.402) significantly exhibited the highest (p < 0.05). There was no significant correlation between water sorption and solubility values for each material (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: The bulk-fill nano-filled composite resin material was successful in terms of water sorption while the bulk-fill glass hybrid restorative system in terms of water solubility. Alkasite can be recommended to be used as a base material due to its high solubility feature. Monomer, filler type, and amount had an impact on the water sorption and solubility properties of the tested materials.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, permitting unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction so long as the original work is properly cited. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Chesterman J, Jowett A, Gallacher A, Nixon P. Bulk-fill resin-based composite restorative materials: a review. Br Dent J. 2017;222(05):337–344. - PubMed
-
- Czasch P, Ilie N. In vitro comparison of mechanical properties and degree of cure of bulk fill composites. Clin Oral Investig. 2013;17(01):227–235. - PubMed
-
- Ilie N, Hickel R. Investigations on a methacrylate-based flowable composite based on the SDR™ technology. Dent Mater. 2011;27(04):348–355. - PubMed
-
- Goracci C, Cadenaro M, Fontanive L et al. Polymerization efficiency and flexural strength of low-stress restorative composites. Dent Mater. 2014;30(06):688–694. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

