A new technique of percutaneous minimally invasive surgery assisted by magnetic resonance neurography
- PMID: 39293800
- PMCID: PMC11410399
- DOI: 10.1302/2633-1462.59.BJO-2024-0018.R1
A new technique of percutaneous minimally invasive surgery assisted by magnetic resonance neurography
Abstract
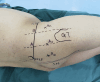
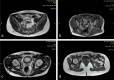
Aims: In order to release the contracture band completely without damaging normal tissues (such as the sciatic nerve) in the surgical treatment of gluteal muscle contracture (GMC), we tried to display the relationship between normal tissue and contracture bands by magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) images, and to predesign a minimally invasive surgery based on the MRN images in advance.
Methods: A total of 30 patients (60 hips) were included in this study. MRN scans of the pelvis were performed before surgery. The contracture band shape and external rotation angle (ERA) of the proximal femur were also analyzed. Then, the minimally invasive GMC releasing surgery was performed based on the images and measurements, and during the operation, incision lengths, surgery duration, intraoperative bleeding, and complications were recorded; the time of the first postoperative off-bed activity was also recorded. Furthermore, the patients' clinical functions were evaluated by means of Hip Outcome Score (HOS) and Ye et al's objective assessments, respectively.
Results: The contracture bands exhibited three typical types of shape - feather-like, striped, and mixed shapes - in MR images. Guided by MRN images, we designed minimally invasive approaches directed to each hip. These approaches resulted in a shortened incision length in each hip (0.3 cm (SD 0.1)), shorter surgery duration (25.3 minutes (SD 5.8)), less intraoperative bleeding (8.0 ml (SD 3.6)), and shorter time between the end of the operation and the patient's first off-bed activity (17.2 hours (SD 2.0)) in each patient. Meanwhile, no serious postoperative complications occurred in all patients. The mean HOS-Sports subscale of patients increased from 71.0 (SD 5.3) to 94.83 (SD 4.24) at six months postoperatively (p < 0.001). The follow-up outcomes from all patients were "good" and "excellent", based on objective assessments.
Conclusion: Preoperative MRN analysis can be used to facilitate the determination of the relationship between contracture band and normal tissues. The minimally invasive surgical design via MRN can avoid nerve damage and improve the release effect.
© 2024 Gao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors received no financial or material support for the research, authorship, and publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Minimally invasive treatment of grade I and II gluteal muscle contracture using a self-made special cutter combined with a specialized compression hemostasis device.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Dec 19;25(1):1024. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08150-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39702133 Free PMC article.
-
Arthroscopic release using F and C method versus conventional open release method in the treatment of gluteal muscle contracture: a comparative study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Mar 16;18(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1484-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28302115 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical efficacy of minimally invasive tendon blade technique in the treatment of moderate and severe gluteal muscle contracture].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2025 Apr 25;38(4):420-3. doi: 10.12200/j.issn.1003-0034.20230406. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2025. PMID: 40296606 Chinese.
-
[Diagnosis and treatment of gluteal muscle contracture associated with unequal leg length caused by pelvis obliquity].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Aug;20(8):835-7. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16955854 Chinese.
-
A neuromuscular clinician's guide to magnetic resonance neurography.Muscle Nerve. 2025 Mar;71(3):293-308. doi: 10.1002/mus.28283. Epub 2024 Oct 31. Muscle Nerve. 2025. PMID: 39479875 Review.
Cited by
-
[Effectiveness analysis of arthroscopic outside-in release for gluteal muscle contracture in supine position].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Jul 15;39(7):848-854. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202504110. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40659588 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Minimally invasive treatment of grade I and II gluteal muscle contracture using a self-made special cutter combined with a specialized compression hemostasis device.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Dec 19;25(1):1024. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08150-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39702133 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

