Diagnostic yield and safety of diagnostic techniques for pulmonary lesions: systematic review, meta-analysis and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 39293856
- PMCID: PMC11409058
- DOI: 10.1183/16000617.0046-2024
Diagnostic yield and safety of diagnostic techniques for pulmonary lesions: systematic review, meta-analysis and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: With recent advancements in bronchoscopic procedures, data on the best modality to sample peripheral pulmonary lesions (PPLs) is lacking, especially comparing bronchoscopy with computed tomography-guided transthoracic biopsy or needle aspiration (CT-TBNA).
Methods: We performed a meta-analysis, pairwise meta-analysis and network meta-analysis on studies reporting diagnostic yield and complications with the use of CT-TBNA, radial endobronchial ultrasound (rEBUS), virtual bronchoscopy (VB), electromagnetic navigation (EMN) or robot-assisted bronchoscopy (RAB) to sample PPLs. The primary outcome was diagnostic yield and the secondary outcome was complications. We estimated the relative risk ratios using a random-effects model and used the frequentist approach for the network meta-analysis. We performed extensive analysis to assess the heterogeneity including reporting bias, publication bias, subgroup and meta-regressional analysis. We assessed the quality of the studies using Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 (QUADAS-2) and QUADAS-Comparative (QUADAS-C).
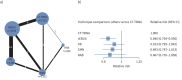
Results: We included 363 studies. The overall pooled diagnostic yield was 78.1%, the highest with CT-TBNA (88.9%), followed by RAB (84.8%) and the least with rEBUS (72%). In the pairwise meta-analysis, only rEBUS showed inferiority to CT-TBNA. The network meta-analysis ranked CT-TBNA as likely the most effective approach followed by VB, EMN and RAB, while rEBUS was the least effective, with a low-GRADE certainty. CT-TBNA had the highest rate of complications.
Conclusion: Although CT-TBNA is the most effective approach to sample PPLs, RAB has a comparable diagnostic yield with a lesser complication rate. Further prospective studies are needed comparing CT-TBNA and RAB.
Copyright ©The authors 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: All authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Noone AMHN, Krapcho M, Miller D, et al. (eds). SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2015. Bethesda, National Cancer Institute, 2018. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2015/
-
- Gould MK, Donington J, Lynch WR, et al. Evaluation of individuals with pulmonary nodules: when is it lung cancer? Diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rd ed: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest 2013; 143: Suppl. 5, e93S–e120S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2351 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
