Unveiling Lobophytum sp. the neuroprotective potential of Parkinson's disease through multifaceted mechanisms, supported by metabolomic analysis and network pharmacology
- PMID: 39294162
- PMCID: PMC11411073
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-66781-9
Unveiling Lobophytum sp. the neuroprotective potential of Parkinson's disease through multifaceted mechanisms, supported by metabolomic analysis and network pharmacology
Abstract
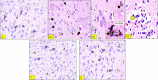
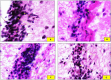
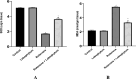
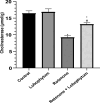
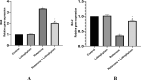
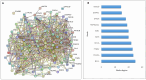
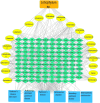
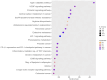
A main feature of neurodegenerative diseases is the loss of neurons. One of the most prevalent neurodegenerative illnesses is Parkinson disease (PD). Although several medications are already approved to treat neurodegenerative disorders, most of them only address associated symptoms. The main aim of the current study was to examine the neuroprotective efficacy and underlying mechanism of Lobophytum sp. crude extract in a rotenone-induced rat model of neurodegeneration mimicking PD in humans. The influence of the treatment on antioxidant, inflammatory, and apoptotic markers was assessed in addition to the investigation of TH (tyrosine hydroxylase) immunochemistry, histopathological changes, and α-synuclein. Metabolomic profiling of Lobophytum sp. crude extract was done by using High-Resolution Liquid Chromatography coupled with Mass Spectrometry (HR-LC-ESI-MS), which revealed the presence of 20 compounds (1-20) belonging to several classes of secondary metabolites including diterpenoids, sesquiterpenoids, steroids, and steroid glycosides. From our experimental results, we report that Lobophytum sp. extract conferred neuroprotection against rotenone-induced PD by inhibiting ROS formation, apoptosis, and inflammatory mediators including IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α, NF-кB, and subsequent neurodegeneration as evidenced by decreased α-synuclein deposition and enhanced tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity. Moreover, a computational network pharmacology study was performed for the dereplicated compounds from Lobophytum sp. using PubChem, SwissTarget Prediction, STRING, DisGeNET, and ShinyGO databases. Among the studied genes, CYP19A1 was the top gene related to Parkinson's disease. Dendrinolide compounds annotated a high number of parkinsonism genes. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway was the top signaling pathway related to the studied genes. Therefore, we speculate that Lobophytum sp. extract, owing to its pleiotropic mechanisms, could be further developed as a possible therapeutic drug for treating Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Lobophytum sp.; Network pharmacology; Neurodegenerative diseases; Parkinson's disease; Rotenone (ROT); VEGF pathway.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Roy, S. P. et al. Antiparkinsonian activity of Tabebuia impetiginosa bark and biochemical analysis of dopamine in rat brain homogenates. In Annales Pharmaceutiques Françaises. (Elsevier, 2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

