Cardiac NAD+ depletion in mice promotes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias prior to impaired bioenergetics
- PMID: 39294272
- PMCID: PMC12498391
- DOI: 10.1038/s44161-024-00542-9
Cardiac NAD+ depletion in mice promotes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias prior to impaired bioenergetics
Abstract
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an essential co-factor in metabolic reactions and co-substrate for signaling enzymes. Failing human hearts display decreased expression of the major NAD+ biosynthetic enzyme nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt) and lower NAD+ levels, and supplementation with NAD+ precursors is protective in preclinical models. Here we show that Nampt loss in adult cardiomyocytes caused depletion of NAD+ along with marked metabolic derangements, hypertrophic remodeling and sudden cardiac deaths, despite unchanged ejection fraction, endurance and mitochondrial respiratory capacity. These effects were directly attributable to NAD+ loss as all were ameliorated by restoring cardiac NAD+ levels with the NAD+ precursor nicotinamide riboside (NR). Electrocardiograms revealed that loss of myocardial Nampt caused a shortening of QT intervals with spontaneous lethal arrhythmias causing sudden cardiac death. Thus, changes in NAD+ concentration can have a profound influence on cardiac physiology even at levels sufficient to maintain energetics.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement
J.A.B is a consultant to Pfizer and Cytokinetics and has received research funding and materials from Elysium Health and Metro International Biotech, both of which have an interest in NAD+ precursors, as well as Calico. D.P.K is a consultant to Pfizer and Amgen. J.D.R. is an advisor and stockholder in Colorado Research Partners, L.E.A.F. Pharmaceuticals, Bantam Pharmaceuticals, Barer Institute, and Rafael Pharmaceuticals; a paid consultant of Pfizer and Third Rock Ventures; a founder, director, and stockholder of Farber Partners, Serien Therapeutics, and Sofro Pharmaceuticals; a founder and stockholder in Empress Therapeutics; inventor of patents held by Princeton University; and a director of the Princeton University-PKU Shenzhen collaboration. The remaining authors have nothing to declare.
Figures


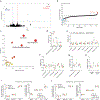

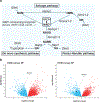
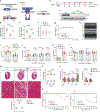


References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL128349/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK127843/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025098/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- TL1TR001880/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01HL128349/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01HL141232/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- T32 AR053461/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL058493/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 HL141232/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK098656/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32HL145923/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- F32 HL145923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32DK127843/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 HL058493/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1DK113643/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- DP1 DK113643/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32AR53461/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- S10-OD025098/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 CA163591/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL165792/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA163591/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- TL1 TR001880/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
