Pathogenic hypothalamic extracellular matrix promotes metabolic disease
- PMID: 39294371
- PMCID: PMC11424483
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07922-y
Pathogenic hypothalamic extracellular matrix promotes metabolic disease
Abstract
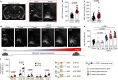
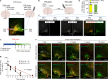
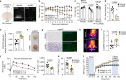
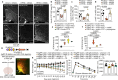
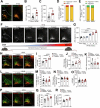
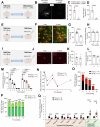
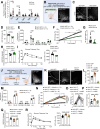
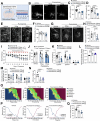
Metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes are marked by insulin resistance1,2. Cells within the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (ARC), which are crucial for regulating metabolism, become insulin resistant during the progression of metabolic disease3-8, but these mechanisms are not fully understood. Here we investigated the role of a specialized chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan extracellular matrix, termed a perineuronal net, which surrounds ARC neurons. In metabolic disease, the perineuronal net of the ARC becomes augmented and remodelled, driving insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction. Disruption of the perineuronal net in obese mice, either enzymatically or with small molecules, improves insulin access to the brain, reversing neuronal insulin resistance and enhancing metabolic health. Our findings identify ARC extracellular matrix remodelling as a fundamental mechanism driving metabolic diseases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
G.T.D, C.A.B. and F.S. hold method-of-use patents for treating insulin resistance and associated disorders (patent numbers WO2024086895 and WO2024113004).
Figures







Comment in
-
Targeting neurofibrosis reverses metabolic dysfunction.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Nov;23(11):813. doi: 10.1038/d41573-024-00156-7. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 39322721 No abstract available.
References
-
- Beddows, C. A. & Dodd, G. T. Insulin on the brain: the role of central insulin signalling in energy and glucose homeostasis. J. Neuroendocrinol.33, e12947 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Dodd, G. T. et al. A hypothalamic phosphatase switch coordinates energy expenditure with feeding. Cell Metab.26, 375–393.e377 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Dodd, G. T., Lee-Young, R. S., Bruning, J. C. & Tiganis, T. TCPTP regulates insulin signaling in AgRP neurons to coordinate glucose metabolism with feeding. Diabetes67, 1246–1257 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Heni, M. et al. Central insulin administration improves whole-body insulin sensitivity via hypothalamus and parasympathetic outputs in men. Diabetes63, 4083–4088 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

