Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and radial peripapillary capillaries density in myopic adults with optical coherence tomography angiography
- PMID: 39294597
- PMCID: PMC11409606
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-024-03673-6
Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and radial peripapillary capillaries density in myopic adults with optical coherence tomography angiography
Abstract
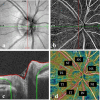
Purpose: To evaluate retinal nerve fiber layer thickness (RNFLT) and radial peripapillary capillaries (RPC) density in adults with different degrees of myopia using optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) and explore their relationship with ocular factors, such as axial length (AL) and disc area.
Methods: A total of 188 subjects were included in this cross-sectional study. The eyes were divided into four groups according to AL. OCTA was used for the assessment of RNFLT, RPC density, and other optic disc measurements, such as disc area. One-way analysis of variance was performed to compare differences between four groups, and P value < 0.01 was considered significant.
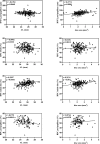
Results: The RNFLT was significantly thinner in high myopia (HM) group at inferior nasal (IN) quadrant (P = 0.004) than low myopia (LM) group, but thicker at temporal inferior (TI) quadrant (P = 0.006). The RPC density of nasal superior (NS) quadrant, nasal inferior (NI) quadrant, and inferior nasal (IN) quadrant significantly decreased as AL increasing. By simple linear regression analysis, the inside disc RPC (iRPC) density tended to be correlated significantly with AL (0.3997%/mm, P < 0.0001). Peripapillary RPC (pRPC) density was in significant correlation with AL (-0.2791%/mm, P = 0.0045), and peripapillary RNFLT (pRNFLT) was in significant correlation with disc area (0.2774%/mm2, P = 0.0001).
Conclusion: RNFLT and RPC density were closely associated with AL and disc area. They might be new indexes in assessing and detecting myopia development via OCTA.
Keywords: Optic disc; Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA); Radial peripapillary capillaries (RPC); Retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL).
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peripheral Superficial Retina Vascular Density and Area of Radial Peripapillary Capillaries Changes in Myopic Individuals: A Wide-Field OCT Angiography Study.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024 Sep 3;13(9):21. doi: 10.1167/tvst.13.9.21. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 39292467 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Analysis of Microvasculature in Macular and Peripapillary Regions in Early Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma.Curr Eye Res. 2020 May;45(5):629-635. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2019.1676912. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Curr Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31587582
-
Quantitative Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography of Radial Peripapillary Capillaries in Glaucoma, Glaucoma Suspect, and Normal Eyes.Am J Ophthalmol. 2016 Oct;170:41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2016.07.015. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Am J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 27470061
-
Characteristics of the radial peripapillary capillary network in patients with COVID-19 based on optical coherence tomography angiography: A literature review.Adv Med Sci. 2024 Sep;69(2):312-319. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2024.07.001. Epub 2024 Jul 6. Adv Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38972386 Review.
-
Axial elongation in nonpathologic high myopia: Ocular structural changes and glaucoma diagnostic challenges.Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2024 Nov-Dec;13(6):100123. doi: 10.1016/j.apjo.2024.100123. Epub 2024 Dec 16. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2024. PMID: 39674402 Review.
Cited by
-
Swept-Source OCT Angiography-Derived Regional Normative Data of Peripapillary Vessel Density in Healthy Populations.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2025 Aug 1;14(8):5. doi: 10.1167/tvst.14.8.5. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40747988 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yekta A, et al. The prevalence of anisometropia, amblyopia and strabismus in schoolchildren of Shiraz. Iran Strabismus. 2010;18(3):104–10. - PubMed
-
- Moriyama M, et al. Topographic analyses of shape of eyes with pathologic myopia by high-resolution three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Ophthalmology. 2011;118(8):1626–37. - PubMed
-
- Koh V, et al. Myopic maculopathy and optic disc changes in highly myopic young Asian eyes and impact on visual acuity. Am J Ophthalmol. 2016;164:69–79. - PubMed
-
- Read SA, et al. Choroidal changes in human myopia: insights from optical coherence tomography imaging. Clin Exp Optom. 2019;102(3):270–85. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

