Altered metabolism in cancer: insights into energy pathways and therapeutic targets
- PMID: 39294640
- PMCID: PMC11409553
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-024-02119-3
Altered metabolism in cancer: insights into energy pathways and therapeutic targets
Abstract
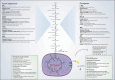
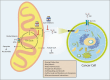
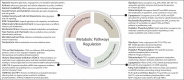
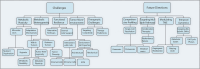
Cancer cells undergo significant metabolic reprogramming to support their rapid growth and survival. This study examines important metabolic pathways like glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, glutaminolysis, and lipid metabolism, focusing on how they are regulated and their contributions to the development of tumors. The interplay between oncogenes, tumor suppressors, epigenetic modifications, and the tumor microenvironment in modulating these pathways is examined. Furthermore, we discuss the therapeutic potential of targeting cancer metabolism, presenting inhibitors of glycolysis, glutaminolysis, the TCA cycle, fatty acid oxidation, LDH, and glucose transport, alongside emerging strategies targeting oxidative phosphorylation and lipid synthesis. Despite the promise, challenges such as metabolic plasticity and the need for combination therapies and robust biomarkers persist, underscoring the necessity for continued research in this dynamic field.
Keywords: Cancer metabolism; Glutaminolysis; Glycolysis; Lipid metabolism; Oxidative phosphorylation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

