Influences of quality of maternal care and environmental enrichment on associative memory function in rats with early life lead exposure
- PMID: 39295102
- PMCID: PMC11410876
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.70040
Influences of quality of maternal care and environmental enrichment on associative memory function in rats with early life lead exposure
Abstract
Introduction: Children in low socioeconomic status (SES) communities are at higher risk of exposure to lead (Pb) and potentially more severe adverse outcomes from Pb exposures. While the factors encompassing SES are complex, low SES households often have less enriching home environments and parent-child interactions. This study investigated the extent to which environmental/behavioral factors (quality of maternal care and richness of the postnatal environment) may modify adverse effects from Pb exposure.
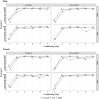
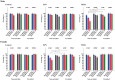
Methods: Long-Evans female rats were randomly assigned to Control (no Pb), Early Postnatal (EPN: birth through weaning), or Perinatal (PERI: 14 days pre-mating through weaning) Pb exposure groups. From postnatal days (PNDs) 2-9, maternal care behaviors were observed, and dams were classified as low or high maternal care based on amounts of licking/grooming and arched back nursing. At weaning, pups were randomly assigned to enriched or non-enriched environments. At PND 55, animals began trace fear conditioning and associative memory was tested on days 1, 2, and 10 postconditioning.
Results: Control offspring showed no significant effects of maternal care or enrichment on task performance. Females with EPN-Pb exposure and males with PERI-Pb exposure living in the non-enriched environment and having an LMC mother had significant memory impairments at days 2 and 10 that were not observed in comparably housed animals with HMC mothers. Enriched animals had no deficits, regardless of maternal care status.
Conclusion: These results show the potential for modulatory influences of maternal care and housing environment on protecting against or reversing at least one aspect of Pb-induced cognitive/behavioral dysfunction.
Keywords: environmental enrichment; lead exposure; maternal care; memory.
© 2024 The Author(s). Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of farrowing crate enrichment strategies on the welfare and performance of sows, suckling piglets, and post-weaned piglets.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf196. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf196. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40598811 Free PMC article.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Planned birth at or near term for improving health outcomes for pregnant women with gestational diabetes and their infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 5;1(1):CD012910. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012910. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29303230 Free PMC article.
-
Antiretrovirals for reducing the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jul 6;(7):CD003510. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003510.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21735394
Cited by
-
Infant cognitive home environment as a moderator for the association of prenatal lead on child language.Neurotoxicology. 2025 May;108:306-317. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2025.04.010. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Neurotoxicology. 2025. PMID: 40280243
-
Developmental lead exposure and aggression in male rats: Influences of maternal care and environmental enrichment.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Jan 30;14:101937. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.101937. eCollection 2025 Jun. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39989979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagot, R. C. , van Hasselt, F. N. , Champagne, D. L. , Meaney, M. J. , Krugers, H. J. , & Joels, M. (2009). Maternal care determines rapid effects of stress mediators on synaptic plasticity in adult rat hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 92(3), 292–300. - PubMed
-
- Bedrosian, T. A. , Quayle, C. , Novaresi, N. , & Gage, F. H. (2018). Early life experience drives structural variation of neural genomes in mice. Science, 359(6382), 1395–1399. - PubMed
-
- Bekinschtein, P. , Oomen, C. A. , Saksida, L. M. , & Bussey, T. J. (2011). Effects of environmental enrichment and voluntary exercise on neurogenesis, learning and memory, and pattern separation: BDNF as a critical variable? Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 22(5), 536–542. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

