Ventral-approach augmented nontransected anastomotic (vANTA) urethroplasty for bulbar urethral strictures: a single-center experience
- PMID: 39295612
- PMCID: PMC11407325
- DOI: 10.55730/1300-0144.5848
Ventral-approach augmented nontransected anastomotic (vANTA) urethroplasty for bulbar urethral strictures: a single-center experience
Abstract
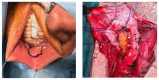
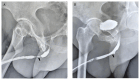
Background/aim: This study describes ventral-approach augmented nontransected anastomotic (vANTA) urethroplasty and presents the preliminary functional results of patients treated with this technique.
Materials and methods: Twenty-three patients who underwent vANTA urethroplasty were included in the study. Stricture location, stricture length, preoperative uroflowmetry parameters (maximum flow rate (Qmax) and mean flow rate (Qmean)), preoperative International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF)-5 scores, operation time, postoperative complications, length of hospital stay, and follow-up periods were recorded. The Qmax, Qmean, and IIEF-5 scores of the patients were recorded again in the second and twelfth postoperative months. Preoperative and postoperative Qmax values and IIEF-5 scores were compared. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed to demonstrate recurrence-free survival.
Results: The mean age of the patients included in the study was 52.1 ± 16.9 years. Mean stricture length was 2.5 ± 0.5 cm. There was a statistically significant difference between preoperative and 2-month postoperative uroflowmetry Qmax values (6.9 (0.0-14.5) vs. 18.5 (5.5-41.5) mL/s; p < 0.001). There was no statistically significant difference in preoperative and 2-month postoperative IIEF-5 scores (p > 0.05). There was a statistically significant difference between preoperative and 1-year postoperative median Qmax values (7.2 (0.0-12.3) vs. 17.4 (11.2-24.3) mL/s; p = 0.001). There was no statistically significant difference between preoperative and 1-year postoperative IIEF-5 scores (p > 0.05). According to Kaplan-Meier recurrence-free survival analysis, the recurrence-free survival rate at 6 months was 95.7.
Conclusion: In cases of bulbar urethral strictures, vANTA urethroplasty is an effective treatment option with limited postoperative complications. Preserving the underlying corpus spongiosum is important to avoid impaired sexual function.
Keywords: Urethral stricture; quality of life; sexual function; urethroplasty; urinary function.
© TÜBİTAK.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Patient-reported outcomes after buccal mucosal graft urethroplasty for bulbar urethral strictures: results of a prospective single-centre cohort study.BJU Int. 2020 Dec;126(6):684-693. doi: 10.1111/bju.15131. Epub 2020 Aug 4. BJU Int. 2020. PMID: 32512634
-
Nontransecting Anastomotic Urethroplasty Via Ventral Approach Without Full Mobilization of the Corpus Spongiosum Dorsal Semicircumference.Urology. 2021 Jun;152:136-141. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2020.10.074. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Urology. 2021. PMID: 33417927
-
Non-transecting dorsal mucosal anastomosis plus ventral oral graft for the treatment of urethral bulbar strictures: single surgeon experience.Int Urol Nephrol. 2022 Dec;54(12):3171-3177. doi: 10.1007/s11255-022-03257-7. Epub 2022 Aug 13. Int Urol Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35962907
-
Substitution urethroplasty using oral mucosa graft for male anterior urethral stricture disease: Current topics and reviews.Int J Urol. 2017 Jul;24(7):493-503. doi: 10.1111/iju.13356. Epub 2017 Jun 10. Int J Urol. 2017. PMID: 28600871 Review.
-
Anterior Urethroplasty for the Management of Urethral Strictures in Males: A Systematic Review.Urology. 2022 Jan;159:222-234. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2021.09.003. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Urology. 2022. PMID: 34537198
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

