Identification and mapping of late blight resistance QTLs in the wild tomato accession PI 224710 (Solanum pimpinellifolium)
- PMID: 39295771
- PMCID: PMC11405559
- DOI: 10.1007/s11032-024-01498-1
Identification and mapping of late blight resistance QTLs in the wild tomato accession PI 224710 (Solanum pimpinellifolium)
Abstract
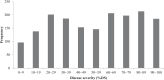
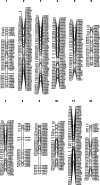
Late blight (LB), caused by oomycete Phytophthora infestans, is one of the most destructive diseases of the cultivated tomato, Solanum lycopersicum. Since new and aggressive clonal lineages of P. infestans, many of which overcoming formerly effective fungicides or host resistance genes, have continued to emerge, it is crucial to identify, characterize, and utilize new sources of host resistance in tomato breeding. A recent screening of tomato germplasm identified Solanum pimpinellifolium accession PI 224710 with very strong resistance to several current P. infestans clonal lineages. The present study aimed to identify and characterize QTLs associated with LB resistance in PI 224710. Disease screening of a large F2 population (n = 1721), derived from a cross between PI 224710 and LB-susceptible tomato breeding line Fla. 8059, followed by F3 progeny testing, resulted in the identification of 43 highly-resistant and 27 highly-susceptible F2 individuals. A selective genotyping approach, using 469 non-identical SNP markers, resulted in the construction of a genetic linkage map and identification of three LB-resistance QTLs on chromosomes 6, 9 and 10 of PI 224710. A comparison of the QTLs genomic locations with the tomato physical map resulted in the identification of several candidate genes, which might be underpinning the LB-resistance QTLs in PI 224710. The identified markers associated with the LB-resistance QTLs can be utilized in breeding programs to transfer resistance from PI 224710 into tomato breeding lines and hybrid cultivars via marker-assisted breeding; they also can be used to develop near-isogenic lines for fine mapping of the QTLs.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s11032-024-01498-1.
Keywords: Disease Resistance; Phytophthora infestans; QTL Mapping; SNP markers; Selective Genotyping; Solanum lycopersicum; Trait-based Analysis; Vertical Resistance.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestThe authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ashrafi H, Kinkade M, Foolad MR (2009) A new genetic linkage map of tomato based on a Solanum lycopersicum x S. pimpinellifolium RIL population displaying locations of candidate pathogen response genes. Genome 52(11):935–956. 10.1139/g09-065 - PubMed
-
- Black LL, Wang TC, Hanson PM, Chen JT (1996) Late blight resistance in four wild tomato accessions: effectiveness in diverse locations and inheritance of resistance. Phytopath 86:S24
-
- Brouwer DJ, Jones ES, St Clair DA (2004) QTL analysis of quantitative resistance to Phytophthora infestans (late blight) in tomato and comparisons with potato. Genome 47(3):475–492. 10.1139/g04-001 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

