Liquiritin ameliorates painful diabetic neuropathy in SD rats by inhibiting NLRP3-MMP-9-mediated reversal of aquaporin-4 polarity in the glymphatic system
- PMID: 39295943
- PMCID: PMC11408323
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1436146
Liquiritin ameliorates painful diabetic neuropathy in SD rats by inhibiting NLRP3-MMP-9-mediated reversal of aquaporin-4 polarity in the glymphatic system
Abstract
Background: Despite advancements in diabetes treatment, the management of Painful Diabetic Neuropathy (PDN) remains challenging. Our previous research indicated a significant correlation between the expression and distribution of Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) in the spinal glymphatic system and PDN. However, the potential role and mechanism of liquiritin in PDN treatment remain uncertain.
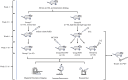
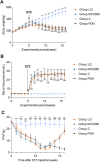
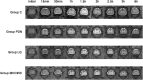
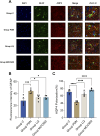
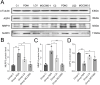
Methods: This study established a rat model of PDN using a combination of low-dose Streptozotocin (STZ) and a high-fat, high-sugar diet. Rats were treated with liquiritin and MCC950 (an NLRP3 inhibitor). We monitored fasting blood glucose, body weight, and mechanical allodynia periodically. The glymphatic system's clearance function was evaluated using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and changes in proteins including NLRP3, MMP-9, and AQP4 were detected through immunofluorescence and Western blot techniques.
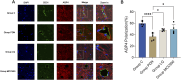
Results: The rats with painful diabetic neuropathy (PDN) demonstrated several physiological changes, including heightened mechanical allodynia, compromised clearance function within the spinal glymphatic system, altered distribution of AQP4, increased count of activated astrocytes, elevated expression levels of NLRP3 and MMP-9, and decreased expression of AQP4. However, following treatment with liquiritin and MCC950, these rats exhibited notable improvements.
Conclusion: Liquiritin may promote the restoration of AQP4 polarity by inhibiting NLRP3 and MMP-9, thereby enhancing the clearance functions of the spinal cord glymphatic system in PDN rats, alleviating the progression of PDN.
Keywords: aquaporin-4; glymphatic system; liquiritin; matrix metalloproteinase-9; painful diabetic neuropathy.
Copyright © 2024 Jia, Yin, Xu, Li, Yan and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aman U., Subhan F., Shahid M., Akbar S., Ahmad N., Ali G., et al. (2016). Passiflora incarnata attenuation of neuropathic allodynia and vulvodynia apropos GABA-ergic and opioidergic antinociceptive and behavioural mechanisms. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 16, 77. 10.1186/s12906-016-1048-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amutha A., Ranjit U., Anjana R. M., Shanthi R. C., Rajalakshmi R., Venkatesan U., et al. (2021). Clinical profile and incidence of microvascular complications of childhood and adolescent onset type 1 and type 2 diabetes seen at a tertiary diabetes center in India. Pediatr. Diabetes 22 (1), 67–74. 10.1111/pedi.13033 - DOI - PubMed
-
- An J., Nichols G. A., Qian L., Munis M. A., Harrison T. N., Li Z., et al. (2021). Prevalence and incidence of microvascular and macrovascular complications over 15 years among patients with incident type 2 diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 9 (1), e001847. 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001847 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

