The efficacy of stereotactic radiotherapy followed by bevacizumab and temozolomide in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma: a case report
- PMID: 39295944
- PMCID: PMC11408163
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1401000
The efficacy of stereotactic radiotherapy followed by bevacizumab and temozolomide in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma: a case report
Abstract
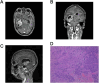
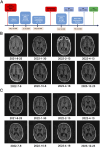
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common and aggressive malignant brain tumor among adults. Despite advancements in multimodality therapy for GBM, the overall prognosis remains poor, with an extremely high risk of recurrence. Currently, there is no established consensus on the optimal treatment option for recurrent GBM, which may include reoperation, reirradiation, chemotherapy, or a combination of the above. Bevacizumab is considered a first-line treatment option for recurrent GBM, as is temozolomide. However, in recurrent GBM, it is necessary to balance the risks and benefits of reirradiation in combination with bevacizumab and temozolomide. Herein, we report the case of a patient with recurrent GBM after standard treatment who benefited from stereotactic radiotherapy followed by bevacizumab and temozolomide maintenance therapy. Following 16 months of concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT), the patient was diagnosed with recurrent GBM by a 3-T contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The addition of localized radiotherapy to the ongoing treatment regimen of bevacizumab, in combination with temozolomide therapy, prolonged the patient's disease-free survival to over 2 years, achieving a significant long-term outcome, with no notable adverse effects observed. This clinical case may provide a promising new option for patients with recurrent GBM.
Keywords: bevacizumab; combination therapy; recurrent glioblastoma; stereotactic radiotherapy; temozolomide.
Copyright © 2024 Zhong, Mao, Wu, Peng and Ye.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ali A. S., Lombardo J., Niazi M. Z., Miller R. C., Alnahhas I., Martinez N. L., et al. (2022). Concurrent chemoradiation and Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields, 200 kHz) for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma: patterns of progression in a single institution pilot study. J. Neuro-Oncology 160 (2), 345–350. 10.1007/s11060-022-04146-w - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

