Sphk1 regulates HMGB1 via HDAC4 and mediates epithelial pyroptosis in allergic rhinitis
- PMID: 39295955
- PMCID: PMC11408713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.waojou.2024.100963
Sphk1 regulates HMGB1 via HDAC4 and mediates epithelial pyroptosis in allergic rhinitis
Abstract
Background: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is a global health issue affecting millions of individuals worldwide. Pyroptosis has emerged as a major player in the development of AR, and targeting its inhibition with specific drugs holds promise for AR treatment. However, a comprehensive understanding of the precise mechanisms underlying pyroptosis in AR remains to be explored, warranting further investigation.
Objective: This study aims to elucidate the roles of HMGB1, Sphk1, and HDAC4 in regulating human nasal epithelial cell (hNEC) pyroptosis and AR.
Methods: An in vitro AR cell culture model and an in vivo AR mouse model were established. Western blot, ELISA, histological staining, and flow cytometry were utilized to confirm the gene and protein expression. The interactions among Sphk1, HDAC4, and HMGB1 were validated through ChIP, Co-IP, and Dual-luciferase assay.
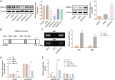
Results and conclusion: We identified that the expression levels of Sphk1, HMGB1, and inflammasome components, including IL-18, and IL-1β were elevated in AR patients and mouse models. Knockdown of Sphk1 inhibited hNEC pyroptosis induced by dust mite allergen. Overexpression of HDAC4 suppressed HMGB1-mediated pyroptosis in hNECs. In addition, HDAC4 was found to mediate the transcriptional regulation of HMGB1 via MEF2C, a transcription factor. Additionally, Sphk1 was shown to interact with CaMKII-δ, promoting the phosphorylation of HDAC4 and inhibiting its cytoplasmic translocation. Knockdown of HDAC4 reversed the effect of Sphk1 knockdown on pyroptosis. These discoveries offer a glimpse into the molecular mechanisms underlying AR and suggest potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of this condition.
Keywords: Allergic; HDAC4; HMGB1; Pyroptosis; Rhinitis; Sphingosine kinase 1.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures






References
-
- Cheng N., Wang Y., Gu Z. Understanding the role of NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis in allergic rhinitis: a review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165 - PubMed
-
- Bousquet J., Melén E., Haahtela T., et al. Rhinitis associated with asthma is distinct from rhinitis alone: the ARIA-MeDALL hypothesis. Allergy. 2023;78(5):1169–1203. - PubMed
-
- Yang Z., Liang C., Wang T., et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation promotes the development of allergic rhinitis via epithelium pyroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;522(1):61–67. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

