Establishment of age-specific reference intervals for serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in a large pediatric population of Nanjing, China
- PMID: 39296073
- PMCID: PMC11408806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37409
Establishment of age-specific reference intervals for serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in a large pediatric population of Nanjing, China
Abstract
Background: The reference intervals (RIs) is defined as the central 95 % range of reference values from healthy individuals. The establishment of appropriate medical RIs for specific populations is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment of disease. However, the RIs for 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in Chinese pediatric individuals are currently not available. This retrospective study aimed to establish pediatric RIs for serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in the Nanjing area of China.
Methods: After data filtering and deletion of outliers, 133,562 serum 25(OH)D records were finally included in this study. The effects of age, sex, and season on 25(OH)D levels were assessed, and the 2.5 % and 97.5 % percentile points were applied as the lower limit and upper limit of the RIs, respectively.
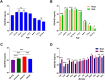
Results: Age-distribution analysis of serum 25(OH)D levels revealed that children aged 4-12 months old hold the highest 25(OH)D levels, and levels subsequently decreased with age while remaining relatively stable in children aged 7-15 years old. An analysis of sex-specific differences demonstrated that serum 25(OH)D levels in girls were significantly higher than those of boys <4 years old (P < 0.001) and dropped to significantly lower than those of boys >7 years old (P < 0.001). Season distribution revealed the highest 25(OH)D levels in autumn, followed by summer and winter, and finally spring. Considering the practicability of clinical application and Z tests according to CLSI C28-A3 guidelines, age-specific RIs for serum 25(OH)D were established. The calculated RIs for children 0-3 months, 4-12 months, 1-3 years, 4-6 years, and 7-15 years old, respectively, were 18.62-42.18, 22.20-45.60, 21.12-45.20, 17.16-38.20, and 15.56-34.39 ng/mL, respectively.
Conclusions: The levels of serum 25(OH)D exhibited statistically significant age and season variations, and the establishment of age-specific RIs for serum 25(OH)D would be beneficial for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Keywords: 25-Hydroxyvitamin D; Age; Children; Reference values; Serum.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age-, season- and gender-specific reference intervals of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 for healthy children (0 ~ 18 years old) in Nanning area of China.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Jan 2;74(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12576-023-00895-z. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38166513 Free PMC article.
-
The establishment of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D reference intervals in children aged 0-14 years in Zigong area, China.J Physiol Anthropol. 2021 Oct 6;40(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s40101-021-00265-x. J Physiol Anthropol. 2021. PMID: 34615548 Free PMC article.
-
Age- and Gender-Specific Reference Intervals for the Fasting Serum Lipid Levels in a Pediatric Population Aged 0-<15 Years in Nanjing, China.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024 Aug 1;31(8):1135-1148. doi: 10.5551/jat.64270. Epub 2024 Feb 28. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2024. PMID: 38417901 Free PMC article.
-
Age- and sex-specific reference intervals for anti-Müllerian hormone during childhood in Chinese population: a cross-sectional study of 2,450 healthy children.Transl Pediatr. 2025 Apr 30;14(4):683-693. doi: 10.21037/tp-2025-104. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Transl Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40386369 Free PMC article.
-
Reference intervals: current status, recent developments and future considerations.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2016;26(1):5-16. doi: 10.11613/BM.2016.001. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2016. PMID: 26981015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources