Quercetin relieves compression-induced cell death and lumbar disc degeneration by stabilizing HIF1A protein
- PMID: 39296087
- PMCID: PMC11408125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37349
Quercetin relieves compression-induced cell death and lumbar disc degeneration by stabilizing HIF1A protein
Abstract
Background: Lumbar disc degeneration (LDD) is a prevalent condition characterized by the decreased viability and functional impairment of nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells (NPMSCs). Shaoyao-Gancao decoction (SGD), a traditional Chinese medicine formula, has been used to treat LDD, but its active components and mechanisms are unclear.
Methods: An integrative network pharmacology and transcriptome analysis were conducted to identify bioactive compounds in SGD that could target LDD. NPMSCs were cultured under mechanical compression as a cellular model of LDD. A rat model of annulus fibrosus needle-puncture was established to induce intervertebral disc degeneration. The effects of quercetin, a predicted active component, on alleviating compression-induced NPMSC death and LDD were evaluated in vitro and in vivo.
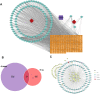
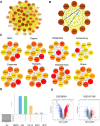
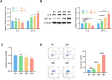
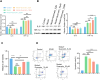
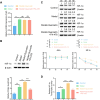
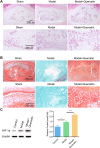
Results: The analysis identified hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF1A) as a potential target of quercetin in LDD. HIF1A was upregulated in degenerated human disc samples and compression-treated NPMSCs. Quercetin treatment alleviated compression-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis, and loss of viability in NPMSCs by stabilizing HIF1A. The protective effects of quercetin were abrogated by HIF1A inhibition. In the rat model, quercetin ameliorated intervertebral disc degeneration.
Conclusion: Our study identified HIF1A as a protective factor against compression-induced cell death in NPMSCs. Quercetin, a bioactive compound found in the traditional Chinese medicine formula SGD, improved the survival of NPMSCs and alleviated LDD progression by stabilizing HIF1A. Targeting the HIF1A pathway through natural compounds like quercetin could represent a promising strategy for the clinical management of LDD and potentially other degenerative disc diseases.
Keywords: HIF1A; Lumbar disc degeneration (LDD); Quercetin; Shaoyao-Gancao decoction (SGD); nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells (NPMSCs).
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Hanaei S., Abdollahzade S., Khoshnevisan A., Kepler C.K., Rezaei N. Genetic aspects of intervertebral disc degeneration. Rev. Neurosci. 2015;26(5):581–606. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

