Limited Impact of Cannabidiol on Health-related Quality of Life of People With Long-term Controlled HIV: A Double-blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial
- PMID: 39296339
- PMCID: PMC11409882
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofae492
Limited Impact of Cannabidiol on Health-related Quality of Life of People With Long-term Controlled HIV: A Double-blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: People with HIV (PWH) with undetectable HIV viral load still have an impaired health-related quality of life (HRQoL). Cannabidiol (CBD) is a nonintoxicating cannabis-derived cannabinoid that holds promise for the treatment of many ailments. In the present study, we tested whether oral CBD-rich medication could significantly improve PWH's HRQoL.
Methods: Eighty participants with undetectable HIV viral load were randomized to either a placebo or full-spectrum CBD (1 mg/kg twice a day) arm for 12 weeks plus a 4-week follow-up period. HRQoL was assessed at baseline, week 12, and week 16 using the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey questionnaire (SF-36). Primary outcomes were physical and mental component summary scores; secondary outcomes were the 8 SF-36 subscale scores. Treatment effects on outcomes were estimated using generalized estimating equations.
Results: We found no effect of CBD intake on the summary score for either component. However, CBD intake was associated with a higher physical functioning score at week 12 only (regression coefficient [95% confidence interval], 7.72 [0.55-14.89]; P = .035). No significant main effect of CBD intake on the other HRQoL subscale scores was observed. Furthermore, there was no difference in self-reported adverse effects between the 2 arms.
Conclusions: Twice-daily CBD full-spectrum oil at 1 mg/kg had no major effect on virologically suppressed PWH's HRQoL but had a positive effect on physical functioning. Further randomized controlled trials including PWH with lower baseline HRQoL are needed to confirm this finding.
Keywords: France; HIV; cannabidiol; quality of life; randomized controlled trial.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interests. H.K. is a paid employee of Little Green Pharma Pty Ltd. This company provided the investigational medicinal product (ie, CBD) and placebo at no financial cost for the purposes of this research. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
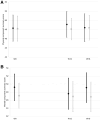
 , cannabidiol group;
, cannabidiol group;  placebo group. Means and 95% confidence intervals are provided. W, week.
placebo group. Means and 95% confidence intervals are provided. W, week.References
-
- Miners A, Phillips A, Kreif N, et al. Health-related quality-of-life of people with HIV in the era of combination antiretroviral treatment: a cross-sectional comparison with the general population. Lancet HIV 2014; 1:e32–40. - PubMed
-
- Engelhard EAN, Smit C, van Dijk PR, et al. Health-related quality of life of people with HIV: an assessment of patient related factors and comparison with other chronic diseases. AIDS 2018; 32:103–12. - PubMed
-
- Nobre N, Pereira M, Roine RP, Sintonen H, Sutinen J. Factors associated with the quality of life of people living with HIV in Finland. AIDS Care 2017; 29:1074–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

