Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway in cancer
- PMID: 39296640
- PMCID: PMC11406677
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.08.002
Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway in cancer
Abstract
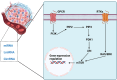
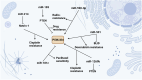
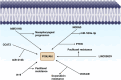
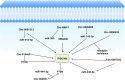
Cancer progression results from the dysregulation of molecular pathways, each with unique features that can either promote or inhibit tumor growth. The complexity of carcinogenesis makes it challenging for researchers to target all pathways in cancer therapy, emphasizing the importance of focusing on specific pathways for targeted treatment. One such pathway is the PI3K/Akt pathway, which is often overexpressed in cancer. As tumor cells progress, the expression of PI3K/Akt increases, further driving cancer advancement. This study aims to explore how ncRNAs regulate the expression of PI3K/Akt. NcRNAs are found in both the cytoplasm and nucleus, and their functions vary depending on their location. They can bind to the promoters of PI3K or Akt, either reducing or increasing their expression, thus influencing tumorigenesis. The ncRNA/PI3K/Akt axis plays a crucial role in determining cell proliferation, metastasis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and even chemoresistance and radioresistance in human cancers. Anti-tumor compounds can target ncRNAs to modulate the PI3K/Akt axis. Moreover, ncRNAs can regulate the PI3K/Akt pathway both directly and indirectly.
Keywords: Cancer progression; Cancer therapy; Chemotherapy; Non-coding RNAs; PTEN; Radiotherapy.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Kashyap D., et al. vol. 125. 2021. pp. 73–120. (Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathways of Apoptosis: Role in Cancer Development and Prognosis). - PubMed
-
- Sung H., et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

